Page 1 (0s)
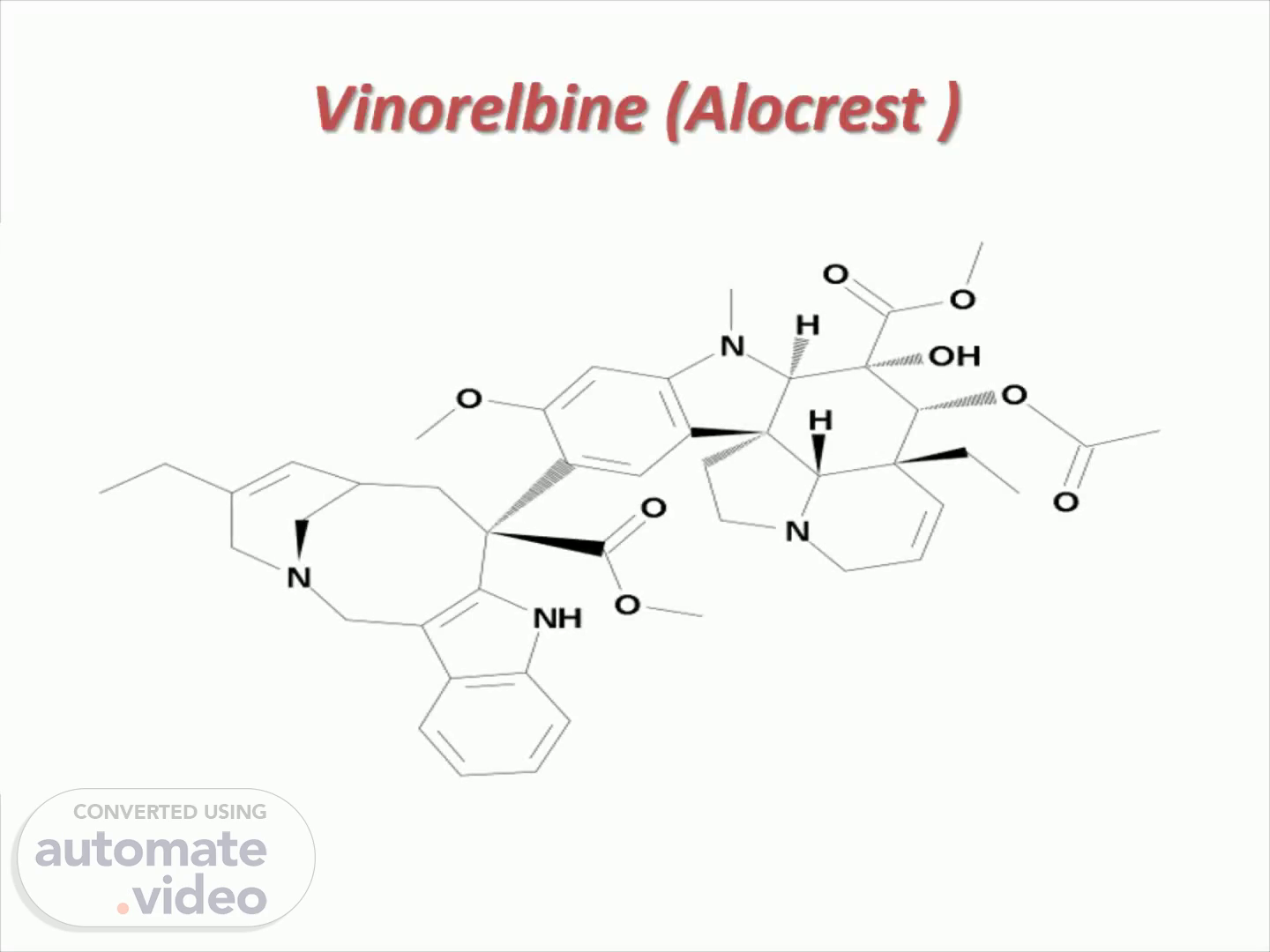
Vinorelbine ( Alocrest ). NH.
Page 2 (1m 23s)
Vinorelbine is a semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid that inhibits cell growth by binding to the tubulin of mitotic microtubules. It has been approved for use as a single agent and in combination with cisplatin for the first-line treatment of unresectable , advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Vinorelbine is also widely used as a treatment for breast cancer. Inex's liposomal drug delivery transmembrane carrier system (TCS), Optisome ™, drug delivery technology utilised sphingomyelin, a biologically inert macromolecule whose amide backbone is resistant to hydrolysis. The increased rigidity of the liposomal walls is designed to prolong the circulating life of liposomes and extend the duration of drug release. In July 2013, Talon Therapeutics was acquired by, and merged into, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals [1] . Prior to its acquisition by Spectrum, the company was exploring options for the continued development of liposomal vinorelbine and was subsequently seeking a partner ..
Page 3 (2m 48s)
Route of administration : IV Formulation : Injection Class : Antineoplastics , Small molecules, Vinca alkaloids Target :Mitosis; Tubulin polymerisation Mechanism of Action : Mitosis inhibitors; Tubulin polymerisation inhibitors WHO ATC code : L01C-A04 ( Vinorelbine ) EPhMRA code : L1C ( Vinca Alkaloids and Other Plant Products) Chemical name : Aspidospermidine-3-carboxylic acid, 4-( acetyloxy )-6,7-didehydro-15-((2R,6R,8S)-4-ethyl-1,3,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-8-( methoxycarbonyl )-2,6-methano-2H-azecino(4,3-b)indol-8-yl)-3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-1-methyl-, methyl ester,(2beta,3beta,4beta,5alpha,12R,19alpha)- Molecular formulaC45 H54 N4 O8 SMILES : N1(C2C(C(C3(C4C2(C2C=C(C(=CC1=2)OC)C1(C2NC5=C(C=2CN2CC(=CC(C1)C2)CC)C=CC=C5)C(=O)OC)CCN4CC=C3)CC)OC(=O)C)(C(=O)OC)O)C.
Page 4 (4m 30s)
Pharmacokinetics In mouse xenograft models of breast and colon cancers, vinorelbine liposomal exhibited a monoexponential decline in plasma levels compared to vinorelbine which showed a rapid decline in plasma concentrations, followed by a slower elimination phase. At the highest dose evaluated, vinorelbine liposomal showed approximately a 70-fold increase in plasma AUC, a 30-fold reduction in drug clearance and a 265-fold reduction in volume of distribution compared with vinorelbine . Increased accumulation of vinorelbine liposomal compared to vinorelbine was observed in MX-1 breast xenograft tumours and tissues of the liver and spleen.
Page 5 (6m 4s)
Adverse Events Solid tumours Phase I preliminary results from a phase I dose-escalation trial with liposomal vinorelbine (60min iv infusion) in patients with solid tumours or with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma showed that the drug was generally well-tolerated. There was no new toxicity relative to conventional vinorelbine . Reversible neutropenia was the most common dose-limiting toxicity . A maximum tolerated dose of 28 mg/m2 (administered via a 60min infusion on days 1 and 8, every 21 days) was established according to updated results from the phase I trial, which recruited 30 subjects.