Scene 1 (0s)
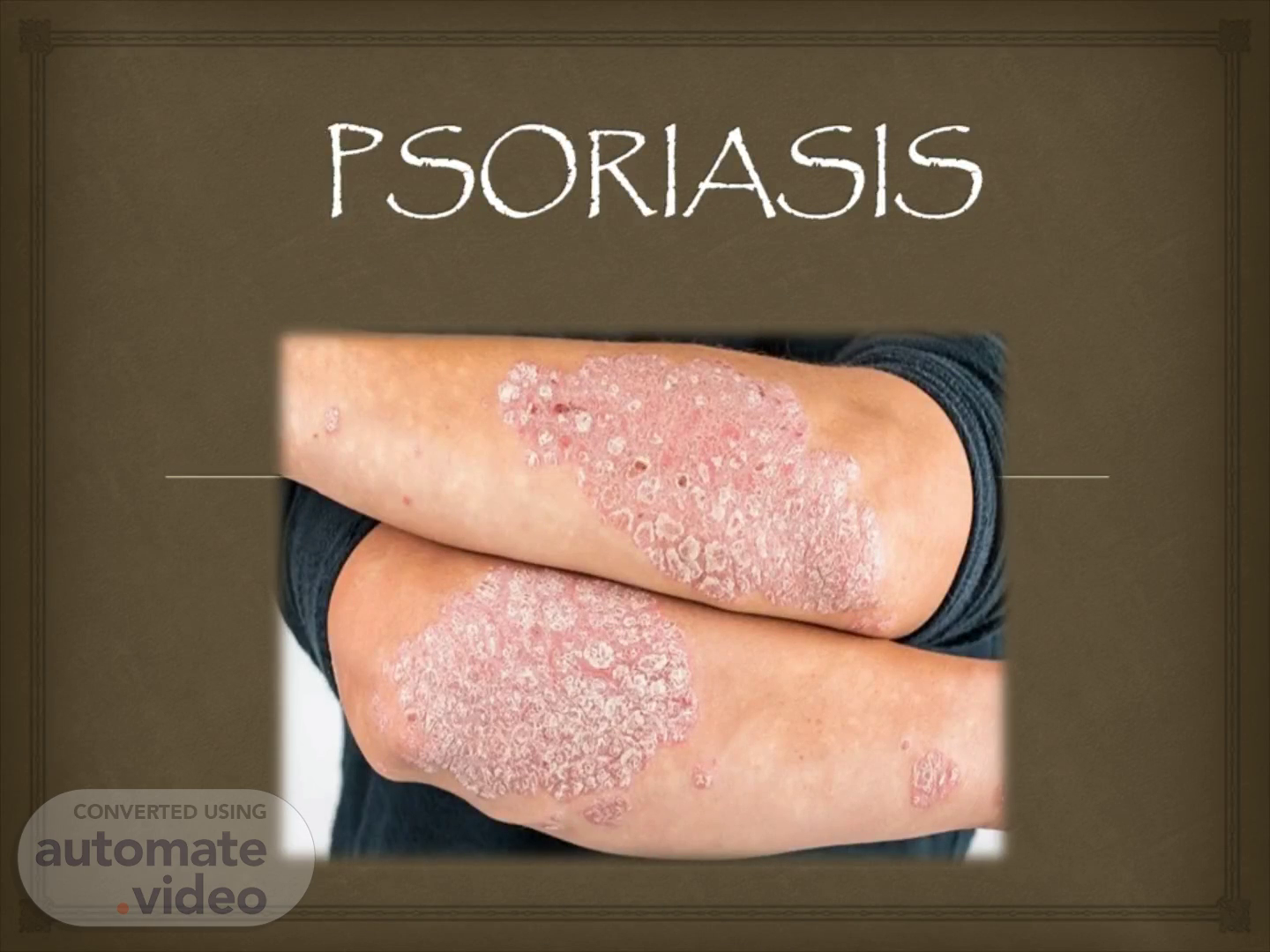
PSORIASIS. .
Scene 2 (9s)
REVIEW ON ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF SKIN. tndine Hair E idermis • relatively waterprcx)f • prevents most tncteria, viruses, and other foreign substances from entering the bcdy produces the pigment melanin that gives huma skin. hair, and eyes their color Dermis • nerve endings: sense pain, touch, pressure, and temperature • sweat glands: in resgx)nse to heat and stress • sebawous glands: secrete sebum into hair follicles. Sebum is an oil, that keeps the skin moist and soft • hair follicles: produæ various Of hair found throughout the bc)dy Fat Layer helps insulate the body trom heat and cold. provides protætive ikldding. and serves as an energy storage area..
Scene 3 (36s)
Immune mediated disorder that occurs when the T lymphocytes attack the healthy skin cells(outer to deepest) Chronic recurrent inflammatory skin disorder. Greek word- “itching condition ” INCIDENCE AND PREVELANCE 125 Million-Worldwide 2.2% population Prevalence varies Developed countries-4.6% of population US- 7.5 Million India- 0.44 to 2.8% population.
Scene 4 (55s)
Idiopathic(unknown) Genetic( HLA Cw6,B13, B17 genes).
Scene 5 (1m 7s)
abstract. CLINICAL MANIFESTATION First sign- Red spot Patchy skin dry, swollen and inflamed Silvery flakes Pain Itching and burning sensation Yellow discoloration(pitting-nails) Cracked and bleeding from the joints Koebner phenomenon.
Scene 6 (1m 23s)
Plaque psoriasis Guttate psoriasis Pustular psoriasis Erythrodermic psoriasis Inversion psoriasis Sebopsoriasis.
Scene 7 (1m 49s)
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION. physical exam biopsy medical history.
Scene 8 (1m 59s)
MANAGEMENT. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT: 1) Topical therapy 2) Emollients and moisturizers What are the drugs used??? Corticosteroids Vitamin D analogues eg . Calcipotriene Coal tar Tazarotene Calcineurin inhibitors- eg . Tacrolimus.
Scene 9 (2m 18s)
Complications * Psoriatic arthritis * Erythrodermic psoriasis.
Scene 10 (2m 37s)
THANK YOU. s.apaoawos ONY au,n0A •oa noth .L8Hm.