Scene 1 (0s)
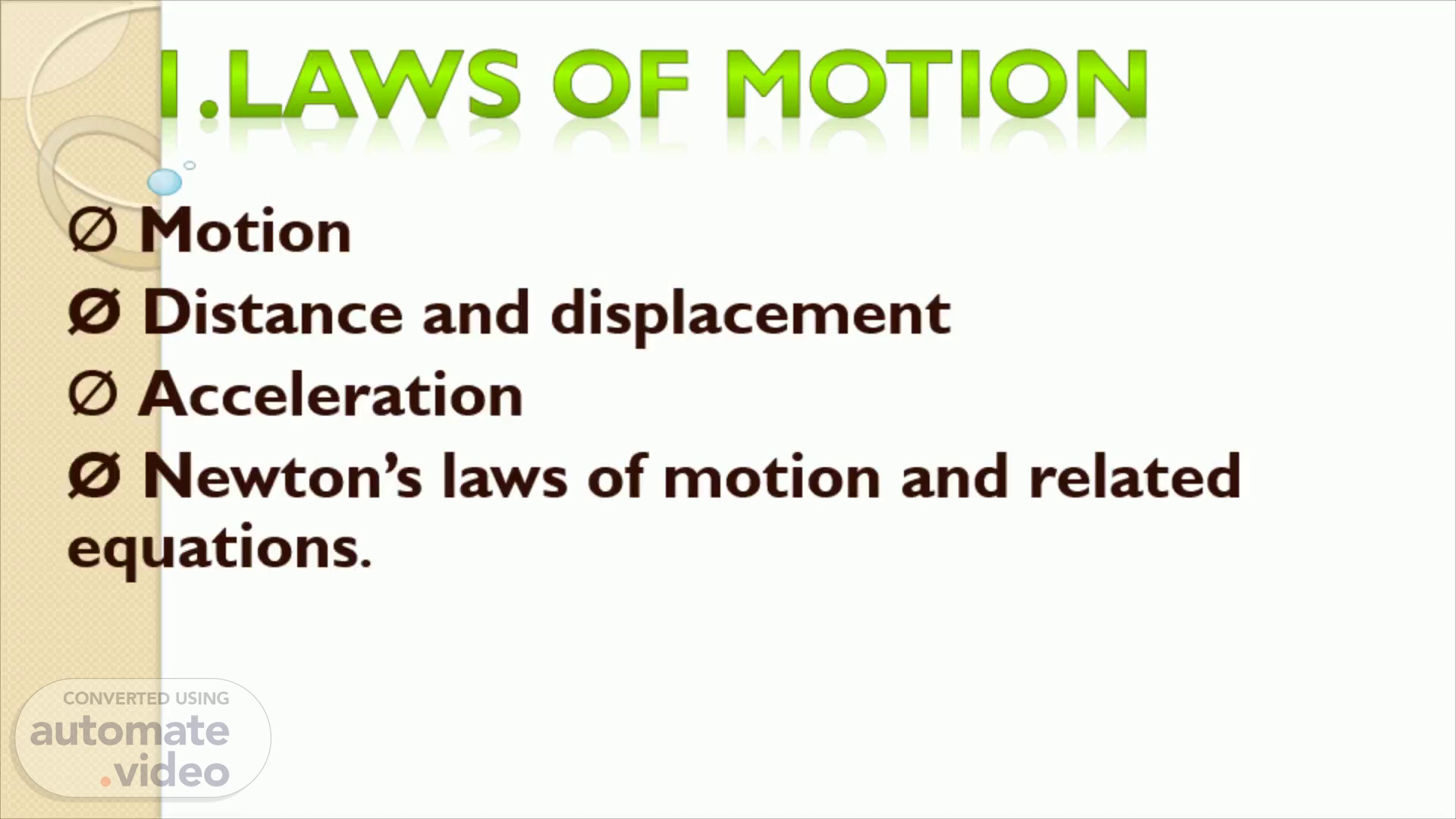
1.LAWS OF MOTION. Ø Motion Ø Distance and displacement Ø Acceleration Ø Newton’s laws of motion and related equations ..
Scene 2 (9s)
Motion of an object. 1.The flight of a bird 2 . A stationary train 3. Leaves flying through air 4. A stone lying on a hill.
Scene 3 (25s)
Think about it.. 1. You are travelling in a bus. Is the person sitting next to you in motion? 2 . What do you take into consideration to decide if an object is moving or not?.
Scene 4 (38s)
M otion is a relative concept.. If the position of an object is changing with respect to its surroundings, then it is said to be in motion. Otherwise, it is said to be at rest..
Scene 5 (53s)
Displacement and distance. B (a) Sheetal and Prashant 's house (b) 500 m Path A School 1200 Path B Sangeeta's house.
Scene 6 (1m 9s)
Displacement and distance. B (a) Sheetal and Prashant 's house (b) 500 m Path A School 1200 Path B Sangeeta's house.
Scene 7 (1m 29s)
‘Distance’ is the length of the actual path travelled by an object in motion while going from one point to another.
Scene 8 (1m 44s)
Even if the displacement of an object is zero, the actual distance traversed by it may not be zero..
Scene 9 (2m 16s)
Can you recall?. 1. What are vectors and scalars? 2 . Which of the quantities distance, speed, velocity, time and displacement are scalars and which are vectors?.
Scene 11 (2m 33s)
Equations of motion using graphical method. v = u + at This is the relation between velocity and time . s = ut +1/2 at2 This is the relation between displacement and time. v2 = u2 + 2as This is the relation between displacement and velocity ..
Scene 12 (3m 2s)
Equation describing the relation between velocity and time.
Scene 13 (3m 31s)
CD = at …… (i) (OC - OD = CD). Draw a line parallel to Y axis passing through B. This will cross the X axis in E. Draw a line parallel to X-axis passing through D. This will cross the line BE at A..
Scene 14 (4m 26s)
Let us suppose that an object in uniform acceleration ‘a’ and it has covered the distance ‘s’ within time ‘t’. From the graph in figure 1.9, the distance covered by the object during time ‘t’ is given by the area of quadrangle DOEB..
Scene 15 (5m 13s)
We have seen that from the graph in figure 1.9 we can determine the distance covered by the object in time t from the area of the quadrangle DOEB. DOEB is a trapezium. So we can use the formula for its area..
Scene 16 (5m 46s)
s = area of trapezium DOEB. s = 1/2 × sum of lengths of × distance between parallel sides the parallel sides.