PowerPoint Presentation
Scene 1 (0s)
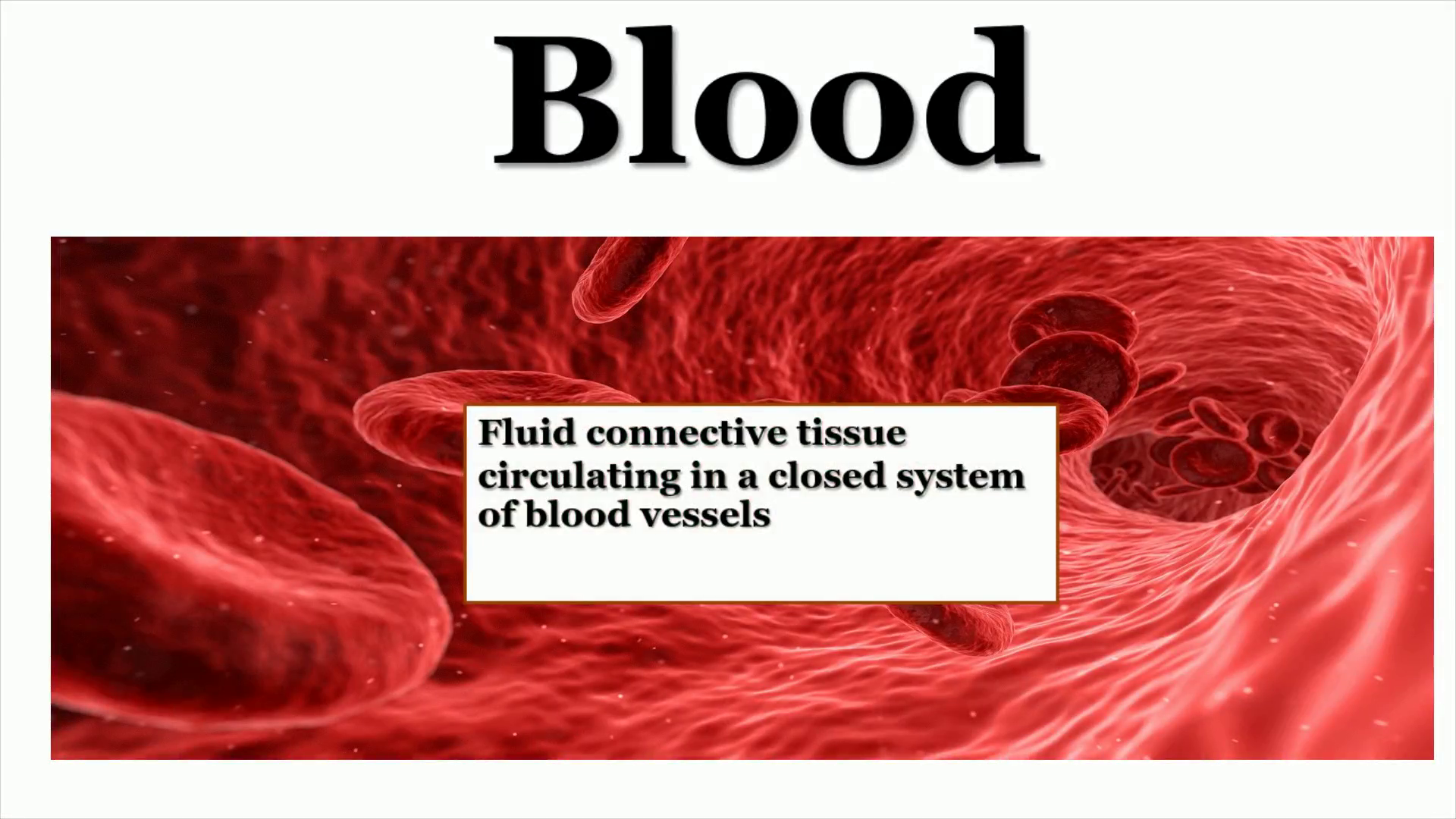
Blood. Blood-based tumor biomarker discovery - Bioanalysis Zone.
Scene 2 (1m 57s)
FUNCTIONS. Transport Respiratory Prevention of hemorrhage Defense Regulatory.
Scene 3 (5m 14s)
3L00b €UNC<IONS PPoTecf10N \RéGULAf10t.a RIGHT 0000 wASfe BL00D.
Scene 4 (5m 29s)
Blood Composition.
Scene 5 (5m 53s)
VL,NSV1d gos.
Scene 6 (7m 39s)
1. Red Blood Cells (RBCs or Erythrocytes) 2. White Blood Cells (WBCs or Leucocytes) 3. Platelets (Thrombocytes).
Scene 7 (8m 21s)
Carrier of O 2 and CO 2 5 * 10 6 /mm 3 Polycythemia Anemia.
Scene 8 (13m 21s)
90 % Water. 10 % solid. Plasma. Non Diffusible. High molecular weight cannot pass the walls of blood vessels e.g. Albumin, Globulin, Fibrinogen Enzymes Nucleoproteins Hormones.
Scene 9 (16m 5s)
O 2. N 2. Gases. CO 2. Dissolved in plasma.
Scene 10 (16m 31s)
Arterial Blood is Red ( oxyhemoglobin ) Venous Blood is Bluish (reduced hemoglobin).
Scene 11 (21m 31s)
the osmotic pressure of Blood is equivalent to 0.9 % NaCl colloidal O.P. (due to plasma proteins) is more effective in water diffusion across capillary walls than Crystalloid O.P. (mainly due to NaCl ).
Scene 12 (26m 31s)
Collection of Blood Specimens. Capillary Blood Collection.
Scene 13 (28m 38s)
Venous Blood Collection.
Scene 14 (28m 57s)
After a pulse is found, a blood sample is taken from the artery.
Scene 15 (29m 29s)
Tools. Disposable. Dry. Precautions in Blood Sampling.
Scene 16 (31m 33s)
After Blood Collection, it’s essential to avoid Hemolysis, especially if serum or plasma is to be used. If hemolysis is not noticeable on inspection, it can be detected spectroscopically by the presence of oxyhemoglobin ..
Scene 17 (33m 48s)
Glucose Lactic acid. Sodium Fluoride used to inhibit glycolysis.
Scene 18 (37m 19s)
It is the conversion of blood from a free flowing liquid SEMISOLID GEL.
Scene 19 (38m 23s)
Clot formation:. Ca 2 +. Platelets.
Scene 20 (39m 10s)
Ca 2+. Platelets. Thrombin. Fibrinogen. Prothrombin.
Scene 21 (39m 43s)
A human blood sample showing red cells (erythrocytes), white cells (leukocytes), platelets (colored yellow/green) and fibrin (light brown). The image was captured by field emission scanning electron microscope and then was colored. https://www.facebook.com/NeuronsWantFood.
Scene 22 (40m 25s)
1) Heparin ( antithrombin ) Prothrombin thrombin 2 ) Dicoumarol ( oral anticoagulant) Prevent synthesis of prothrombin due to structural similarity with vitamin K 3) Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid chelate Ca ++ 4) Oxalate precipitate Ca ++ 5) Sodium citrate convert Ca ++ to non-ionized form 6) Sodium fluoride Act as anticoagulant but large amount are required. It is used mainly as preservative (by inhibition of RBCs metabolism and bacterial action ).
Scene 23 (43m 32s)
Blood (anticoagulant) Water bath 37 Centrifuge. Blood + anticoagulant Centrifuge.
Scene 24 (45m 47s)
Differences between Plasma and Serum. Plasma Serum Preparation Blood + anticoagulant then centrifuge Blood without anticoagulant then centrifuge Thrombin Absent Present Injection Can be injected Never injected Fibrinogen Present Absent Prothrombin Present Absent Addition of xss Ca ++ Clotting No clotting.
Scene 25 (49m 34s)
Carboxyhemoglobin Hemoglobin Lactate pH Pyruvate.
Scene 26 (51m 18s)
Hematocrit Value (HV) Or Packed Cell Volume (PCV).
Scene 27 (52m 14s)
Wintrobe tube.
Scene 28 (53m 9s)
Dehydration. Normal HV values 45% for adult male 35% for adult female 25% for children 65% for new born.
Scene 30 (1h 1m 25s)
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate ( ESR ). Experiments on Blood.
Scene 31 (1h 3m 8s)
Westergren tube. One hour later C 2009 American colle of Rheumat(.
Scene 32 (1h 4m 30s)
Physiologically. Normal ESR Male up to 19 mm/ hr Female up to 15 mm/ hr Children up to 13 mm/ hr.
Scene 33 (1h 6m 45s)
Fragility test. It’s the resistance of RBCs to hypotonic solutions In normal human, complete hemolysis occurs only below about 0.35% NaCl . i.e. RBCs resist hemolysis above 0.45%.
Scene 34 (1h 11m 45s)
Hypertonic ooo Isotonic Hypotonic.
Scene 35 (1h 14m 7s)
crenated HYPERTONIC normal swollen lysed VERY ISOTONIC HYPOTONIC HYPOTONIC.
Scene 36 (1h 15m 27s)
Prepare a series of hypotonic NaCl solutions. 0.3% NaCl 0.4% NaCl 0.45% NaCl 0.5% NaCl 0.6% NaCl 0.7% NaCl 3 ml 4 ml 4.5 ml 5 ml 6 ml 7 ml 1% NaCl solution 7 ml 6 ml 5.5 ml 5 ml 4 ml 3 ml Distilled water.
Scene 37 (1h 18m 16s)
Transparent tubes indicates Hemolysis Translucent tube indicates Partial Hemolysis.
Scene 38 (1h 23m 16s)
Effect of Different Hemolytic Agents. 0.1 N NaOH.
Scene 39 (1h 23m 46s)
Formation of brown Alkaline Hematin. Formation of brown Acid Hematin.
Scene 40 (1h 27m 19s)
Determination of hemoglobin. Determine the oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
Scene 41 (1h 28m 19s)
Acid Hematin Method ( Sahli ’ s method ). Blood. dil. Acid.
Scene 42 (1h 29m 9s)
Sahli ’ s Hemometer. Sahli Type Haemoglobin Meter, Digital Hemoglobinometer, Hemoglobin Test Machine, Hemoglobin Monitor, Hb Meter, Hemoglobin Check Machine in Industrial Estate, Ambala , Laby Instruments Industry | ID: 15672891530.
Scene 43 (1h 31m 28s)
Colorimetric method ( Drabkin ’ s reagent). Drabkin ’ s reagent.
Scene 44 (1h 33m 42s)
Sahli ’ s method Drabkin ’ s method Visual method Colorimetric method Subjective Objective Less accurate More accurate 0.1 N HCl ( reagent ) Drabkin ’ s reagent Acid hematin (product ) Cyano Met Hb (product ).
Scene 45 (1h 36m 2s)
Normal Hemoglobin values Female : 12-16 g/dl (70-110%) Male : 14-18 g/dl (80-120 %).
Scene 46 (1h 37m 29s)
O Thank you.