Scene 1 (0s)
[Audio] Good morning everyone. Today's topic is the male reproductive system. This complex system consists of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, associated glands and external genitalia. The primary sex organs are a pair of testes, which are a very important part of the reproductive system. The testes are oval in shape and measure about 4 to 5 cm in length, 2-3 cm in width and about 3 cm in thickness. They are covered with a dense covering called the tunica albuginea. Inside the testes, they are divided into about 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each of these lobules contains one to three highly coiled seminiferous tubules which are the structural and functional units for sperm production. Finally, the interstitial spaces between the seminiferous tubules contain blood vessels and Leydig cells which produce the male sex hormone testosterone. Paying attention?.
Scene 2 (1m 7s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system consists of a duct system, which includes the tubuli refti, vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct and urethra. These structures provide the transportation of sperm from the testes to the external environment. In addition to this duct system, the system also consists of several accessory glands, including a pair of seminal vesicles, a prostate gland, and a pair of bulbourethral glands. These glands produce seminal plasma, a substance which is a combination of fructose, calcium, and enzymes. This seminal plasma provides nutrition and a medium for the spermatozoa to swim in the female reproductive tract. The system is also composed of a number of external genitalia, including the penis. Cilia, present in the vasa efferentia, also play an important role in the physiological maturation of sperms. This overview of the parts and function of the human male reproductive system should help to better understand this vital system..
Scene 3 (2m 20s)
[Audio] I'd like to discuss the human reproductive system. In males, the external genitalia is the penis, which is made up of special erectile tissue to aid insemination. It contains the glans penis and is covered by a loose fold of skin known as the foreskin or prepuce. The female reproductive system is composed of the primary sex organ, the ovaries, and the secondary sex organs, including the duct system. This is composed of the fallopian tubes, the uterus, cervix and vagina, as well as external genitalia and mammary glands. The ovaries produce female gametes and secrete ovarian or sex hormones. The mammalian testes contain Leydig cells which are not found in the testes of frogs. Any questions?.
Scene 4 (3m 14s)
[Audio] In this presentation, we will focus on the human male reproductive system, which consists of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. Turning to the reproductive duct system, a fallopian tube extends from the periphery of each ovary to the uterus. This tube is about 10-12 cm long and is situated above and behind the urinary bladder. The part of the fallopian tube closest to the ovary is called the infundibulum and has finger-like projections called fimbriae which help in collecting the ovum during ovulation. This infundibulum leads into the ampulla, which is the wider part of the fallopian tube, which ultimately connects to the uterus via the isthmus. To summarize, the part of the fallopian tube closest to the ovary is the infundibulum and from a secondary spermatocyte, 8 sperms are formed..
Scene 5 (4m 13s)
[Audio] In the male reproductive system, the primary sex organ is the testes which produce the sperm. The secondary sex organs are the epididymis, vas deferens, and prostate gland, all producing fluids to transport the sperm. External genitalia include the penis, scrotum, and urethra. In the female reproductive system, the primary sex organ is the ovaries and the uterus is an inverted pear-shaped muscular structure attached to the pelvic wall and supported by ligaments. It consists of three layers - perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium - with the myometrium's contractions responsible for parturition. External genitalia include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, and clitoris, with the vagina serving as the birth canal, partially covered by the hymen. The pathway for sperm transport from the rete testis to the epididymis is rete testis → efferent ductules → epididymis → vas deferens..
Scene 6 (5m 23s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system is composed of several organs that work together to produce and deliver sperm. The primary sex organs are the testes and epididymides, responsible for the production of sperm cells, and the secondary sex organs are the accessory glands, like the seminal vesicles and prostate, which secrete other components to produce semen. External genitalia, such as the penis and scrotum, also plays an important role in the male reproductive system. The female reproductive system consists of primary and secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. The labia majora are a pair of fleshy folds of tissue that surround the vaginal opening while the labia minora are paired folds of tissue below the labia majora that enclose the vaginal opening. The hymen is a membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening and is usually ruptured with vigorous physical activity or during the first coitus. The female reproductive system also includes the mammary glands, which are functional glands consisting of glandular tissues and varying amounts of fat. Milk is secreted and stored in the lumen of the alveoli present in the mammary ducts and can be expelled through a lactiferous duct. In males, spermatogenesis is the process of sperm formation in the seminiferous tubules and starts at puberty. Spermatogonial cells divide by mitosis, with some functioning as stem cells and others as progenitor cells or precursors of spermatozoa. All of these organs and processes must work together in order for reproductive success..
Scene 7 (7m 9s)
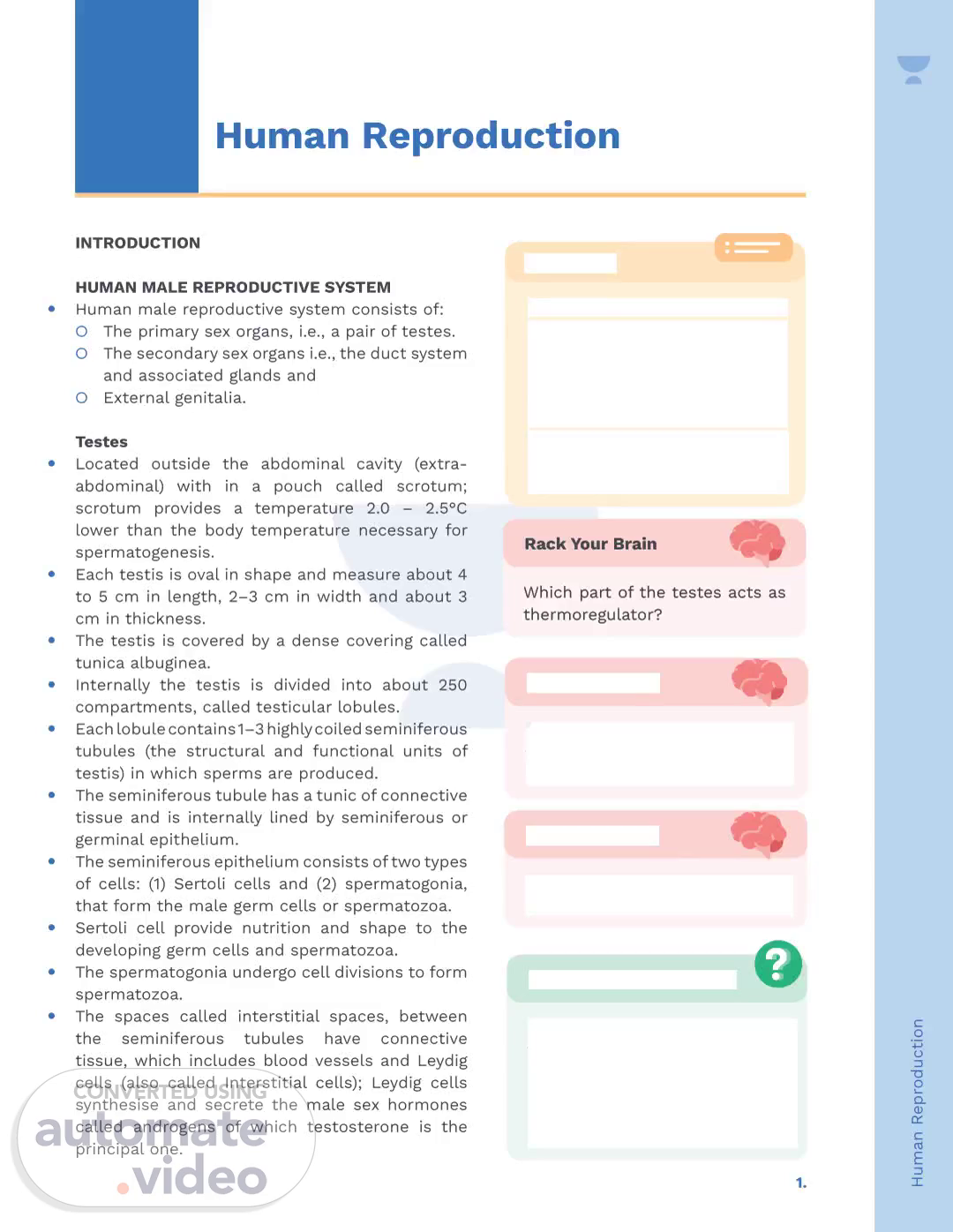
7.. Human Reproduction. y They undergo changes by accumulating food materials and grow almost double in size and become the primary spermatocytes..
Scene 8 (7m 36s)
[Audio] Human sperms have a structure and function which is crucial to the reproductive process. Spermatogenesis is initiated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) at puberty, which triggers the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). LH acts on the Leydig cells to produce testosterone while FSH acts on the Sertoli cells which facilitates spermiogenesis. The four components of a human sperm are the head, neck, middle piece and tail. The head contains a haploid nucleus and the acrosome which houses enzymes important for fertilization. The neck has two centrioles, of which one is essential for the first division of a zygote, and the other is linked to the tail filament. The middle piece has mitochondria which provide energy needed for motility. The viability of human sperm is 24 hours..
Scene 9 (8m 40s)
[Audio] Follicular atresia is an important process in the female reproductive system, occurring before puberty. It is the degeneration of a large number of follicles in the ovary. The human male reproductive system comprises of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, glands and external genitalia. A vital element of this system is the tail of the sperm, which is an axial filament surrounded by plasma membrane. This aids in sperm motility, or the ability to move towards the female gamete, or ovum, to enable fertilization. Oogenesis is the formation of female gametes or ova in the ovary. It starts in the female foetus, when around one million oogonial cells are formed. This involves the formation of a primary follicle, which is encased in granulosa and thecal layers, and the development of an antrum. The primary oocyte then undergoes meiosis I and forms the secondary oocyte and a small cell, the first polar body. Therefore, the male reproductive system and its interconnected elements are essential for fertility, with follicular atresia playing a key role..
Scene 10 (9m 59s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. The female anatomy also consists of a primary reproductive cell, known as the secondary oocyte. It develops in size as it absorbs nutrients and forms a Graafian follicle. To protect itself, a new membrane called the zona pellucida is generated. During gametogenesis, the secondary oocyte commences its second meiotic division, but remains stalled in metaphase II until a sperm penetrates it. Subsequently, the Graafian follicle ruptures and the secondary oocyte is expelled from the ovary. The correct answer to the question from the previous year is option (1), spermatogonia, which is a diploid cell during gametogenesis..
Scene 11 (10m 57s)
11.. Human Reproduction. MENSTRUAL CYCLE. y The cyclic changes that occur in the reproductive organs of primate females (monkeys, apes and human beings), constitute the menstrual cycle..
Scene 12 (11m 59s)
[Audio] The human reproductive system is comprised of primary and secondary sex organs, paired with glands and external genitalia. During the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, the Graafian follicle ruptures and the contents transform into a corpus luteum. This corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone, which is vital for the sustainment and thickening of the endometrium. Additional glands secrete fluids into the uterus in the event of fertilization. In the event fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum deteriorates, resulting in the endometrium breaking down and thereby initiating menstruation. A question presented in the previous year asked what the Graafian follicle regresses into, the answer being corpus luteum..
Scene 13 (12m 52s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system includes primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands. The primary sex organs are the testes, which are responsible for the production of sperm. The secondary sex organs include the penis, and the associated glands are the seminal vesicles and prostate gland which produce the seminal fluid that carries the sperm. At menopause, which typically occurs around the age of 45-50, the female's menstrual cycles cease. During copulation, the semen of the male is released into the female's vagina via the penis; this is known as insemination. The motile sperm then travel through the cervix, into the uterus and eventually to the ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube. Here, the ovum, which has been released from the ovary, also awaits and is joined by the sperm for the process of fertilization. As the sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum, various changes occur in the membrane which only allows entry of one sperm into the ovum. The enzymes in the sperm's acrosome help to dissolve the zona pellucida and plasma membrane of the ovum, allowing the sperm to enter the ovum's cytoplasm. This triggers the completion of the second meiotic division of the ovum, thus forming a haploid ootid and a small second polar body. Overall, the human reproductive system's function is to create new life and ensure the continuity of life on earth..
Scene 14 (14m 33s)
[Audio] The development of the human zygote is an incredible process. After fertilization, it divides multiple times to become an embryo through a process known as cleavage. This results in a morula, an embryo composed of 16 or fewer blastomeres. As it continues to divide, the blastomeres arrange themselves around the edge of the embryo to form a hollow sphere called the blastocyst. This blastocyst consists of an outer layer, the trophoblast, and an inner group of cells, the inner cell mass. Finally, it becomes implanted in the uterus, the final step in embryonic development. Comprehending the process is essential to comprehend human reproduction and development..
Scene 15 (15m 22s)
[Audio] Good afternoon, everyone. At this stage of the presentation, we will be discussing the human male reproductive system. This includes the primary and secondary sex organs, along with associated glands and external genitalia. After fertilization, the trophoblast cells attach itself to the endometrium, and the cells of the endometrium divide rapidly to cover the blastocyst—this process is called implantation and leads to pregnancy. Interdigitated between the chorionic villi and the uterine tissue is the placenta which is the structural and functional unit between the embryo and the uterine wall of the mother. The umbilical cord connects the placenta with the foetus and allows for transport of substances to and from the foetus. The placenta also secretes hormones, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), progestogens, and estrogens, which are necessary for the foetal growth and maintenance of pregnancy. Additionally, the levels of other hormones such as estrogens, prolactin, and thyroxine also significantly increase in the material blood. Finally, the inner cell mass of the blastocyst will differentiate into an outer layer, called ectoderm, and an inner layer called endoderm. I will define three terms: LH-surge, umbilical cord, and implantation. LH-surge is the maximum level of LH during the middle of the menstrual cycle. The umbilical cord is the cord-like structure that connects the placenta to the foetus. And, implantation is when the embryo gets attached to the endometrium..
Scene 16 (17m 16s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. The development of the male reproductive system begins with the primary germ layers which give rise to all the tissues and organs in the adult. By the third month, or first trimester, of pregnancy most organ systems are formed, and by the end of the second trimester body hair and eyelashes have formed. Finally, by the end of the pregnancy, the male reproductive system has developed fully, with external genitalia and associated glands. It is thanks to this system that we have all come to be here today..
Scene 17 (18m 0s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system is made up of the primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, related glands and external genitalia. At eight months of pregnancy, the testes descend into the scrotum. In the ninth month, foetal development is completed and a hormone called relaxin is released, enabling loosening of the connective tissues and preparation for childbirth. Pregnancy typically lasts nine months with the mother's body producing hormones to make labour occur. The womb and placenta give signals that activate a reflex which brings about mild uterine contractions and the secretion of the hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin stimulates the uterine muscles leading to stronger contractions and delivery of the baby..
Scene 18 (18m 50s)
[Audio] The Human Male Reproductive System consists of the primary sex organs, secondary sex organs and associated glands and external genitalia. After parturition, the mammary glands of the mother produce milk, known as Colostrum, which contains numerous antibodies to help the new-born build immunity. Oxytocin is the hormone responsible for the ejection of milk from the mammary glands after the delivery of the infant..
Scene 19 (19m 18s)
[Audio] The human male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. The primary sex organs are the testes, which produce sperm and testosterone. The secondary sex organs are the penis, which transports sperm during ejaculation, and the scrotum, which is a sac that contains and protects the testes. The associated glands are the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands, which produce semen to aid in the fertilization of an egg. The external genitalia are the penis, scrotum, and pubic hair." "The human male reproductive system consists of a variety of organs and glands. The testes are the primary sex organs, producing sperm and the male hormone testosterone. The secondary sex organs are the penis, which is used for sperm transport during ejaculation, and the scrotum, which is a sac that holds and protects the testes. Associated glands are the seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands which create semen to help fertilize an egg. The external genitalia are the penis, scrotum, and pubic hair..
Scene 20 (20m 39s)
[Audio] Human males have a reproductive system consisting of organs and structures essential for creating offspring. This slide focuses on anatomy of the male reproductive system and how it leads to sperm production and delivery. Specifically, the testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum. This unique external location helps keep the testes at a lower temperature than the body's internal temperature, allowing for optimal sperm production. Additionally, the vasa efferentia are responsible for transferring gametes from the testes to the epididymis. If the vasa efferentia become blocked, it hinders the transportation of gametes from the testes to the epididymis..
Scene 21 (21m 26s)
[Audio] The male human reproductive system is made up of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, associated glands and external genitalia. After the first meiotic division, male germ cells develop into secondary spermatocytes. These cells, along with Sertoli cells positioned in the germinal epithelium of the seminiferous tubules, create spermatids. For the female human, the blastocyst or early-stage embryo is implanted in the uterus by the trophoblast cells. After implantation, the blastocyst gets nutrition from the endometrial secretions of the uterus via the trophoblast layer..
Scene 22 (22m 10s)
[Audio] Humans possess a reproductive system consisting of primary sex organs, secondary sex organs, and associated glands and external genitalia. The primary sex organs, the gonads, develop from the mesoderm layer in the embryo and are responsible for producing the reproductive cells needed for sexual reproduction. In adults, these are the testes in males and the ovaries in females. Secondary sex organs transport and store gametes, with male organs including the vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland, and female organs including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina. Associated glands and external genitalia are also present to release hormones that regulate the reproductive process, with examples being the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, mammary glands, penis, scrotum, clitoris, and labia..
Scene 23 (23m 9s)
[Audio] The egg plays a key role in the human reproductive system. It is haploid, meaning it only contains one X-chromosome and 22 autosomes. During the 28 day ovarian cycle, the graafian follicle ruptures on day 14, allowing the egg to enter the Fallopian tube. This event is crucial for understanding the complexity of the reproductive system..