Page 1 (0s)
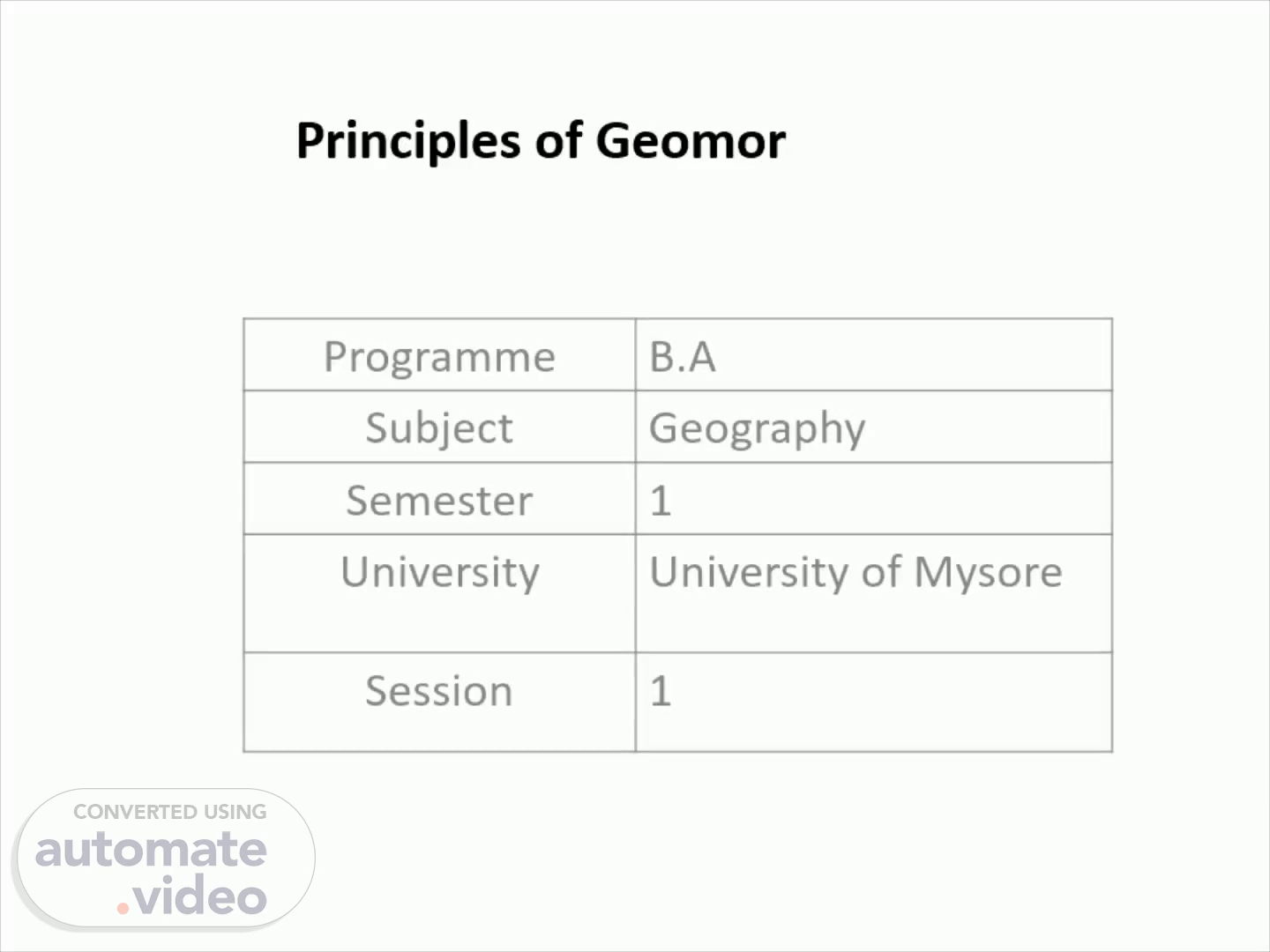
Principles of Geomorphology. Programme B.A Subject Geography Semester 1 University University of Mysore Session 1.
Page 2 (8s)
UNIT-1 : Geomorphology. Introduction of geography : Physical and Human Geography.
Page 3 (16s)
Learning objectives of the chapter. Students will be able to define geography and be able to describe in good detail the major subdivisions of the field of geography. explain what geographers do; and how geography relates to a variety of real-world jobs (all majors). This chapter introduces Geography and one of it's main branches,.
Page 4 (33s)
Learning outcome. By the end of this course, the student will: Students will acquire an understanding of and appreciation for the relationship between geography and culture. Students will acquire an understanding of and appreciation for the role that geography can play in community engagement..
Page 5 (49s)
The word 'Geography' is coined from two Greek words, 'Geo' means earth and ' Graphien ' means description . Thus Geography is concerned with describing of the earth surface. It is believed that the term Geography was first used by a Greek Geographer, Eratosthenes (276-194 B.C) . So he is aptly considered as the 'Father of Geography' . Geography deals with both the natural and man made features of the earth surface. Accordingly, the field of Geography is divided into two broad divisions namely Physical Geography and Human Geography..
Page 6 (1m 14s)
Physical Geography : It is one of the two major divisions of Geography. It is concerned with the study of the natural features of the earth's surface which are broadly grouped into four components, namely Lithosphere, Atmosphere, Hydrosphere and Biosphere . These four spheres are interrelated and have produced the varying physical or natural environment of the earth. The surface features are highly variable from one place to another. It is mainly attributed to the variation of these four components of the physical environment. The study of earth's surface is the subject matter of Physical Geography. The term physical Geography was first used by Immanuel Kant (1724-1804 A.D.) of Germany ..
Page 7 (1m 44s)
Human Geography: Human Geography is the second main division of Geography. The Word Human Geography was coined by Friedrich Ratzel of Germany through his book ' Anthropo Geography' in 1882..
Page 8 (1m 57s)
Development of Geography: Geography has a long history of more than 3000 years. It is one of the oldest disciplines. It is believed that Eratosthenes (276-194 B.C.), a librarian in the ancient city of Alexandria, (Egypt) has written a book ' Geographia ' which contained the word Geography . During the Greeko -Roman period, the geographical knowledge of man was largely confined to the shore lands of the Mediterranean sea in the west and to the north-western parts of India in the east..
Page 9 (2m 21s)
The word geography was used to denote the list of names, like mountains, rivers, boundaries of countries, cities, etc of the known Part of the Earth called ' ecumene ' while the unknown areas were called 'terra incognita'. So geography of this ancient period was in Gazetteer form containg list of place names, hills, rivers etc..
Page 10 (2m 51s)
Through geographical explorations man acquired enormous knowledge about different parts of the world as well as the nature of human life and their means of adaption to their environment. He had also noticed an integrated relationship between the mode of human life and the environment. Geographers have adopted "comparative method" for the study of different areas of the world. Modern geography was developed in Germany systematically by the contributions of Alexander Von Humbolt (1769- 1859) Karl Ritter (1779-1859) Alfred Hettner (1859-1941) and Friedrich Ratzel (1844-1904). In France Vidal de-la Blache (1848 - 1918) has lead the development of the geography..
Page 11 (3m 18s)
Geographers during 18th and 19th centuries have concentrated on the description of human life in different parts of the world in relation to the natural environment. The study of man was also included within the ambit of geography. Geography was thus defined as the study of the earth as the home of man. Geography has borrowed material of study from many social, physical and biological sciences and analysed to give them a spatial dimension means how they are distributed on the earth's surface. Thus, it is on of the most important interdisciplinary subjects..
Page 12 (3m 44s)
SUMMARY. Geography is the study of places and the relationships between people and their environments . Geographers explore both the physical properties of Earth's surface and the human societies spread across it. Geography helps us to explore and understand space and place - recognising the great differences in cultures, political systems, economies, landscapes and environments across the world, and exploring the links between them.
Page 13 (4m 3s)
Sources and References. Baulig , Henri (1950). Essais dc geomorphologie . Publs , de la faculté de l'université de Strasbourg, Paris, p. 35. Chorley, R. J., A. J. Dunn, and R. P. Beckinsale (1964). The History of the Study of Landforms, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 678 pp. Fenneman , N. M. (1939). The rise of physiography ), Bull. Geol. Soc. Am., 50, pp. 349-360. Hack, J. T. (1960). Interpretation of erosional topography in humid temperate regions, Am. J. Sci., 258-A, pp. 80-97..