Scene 1 (0s)
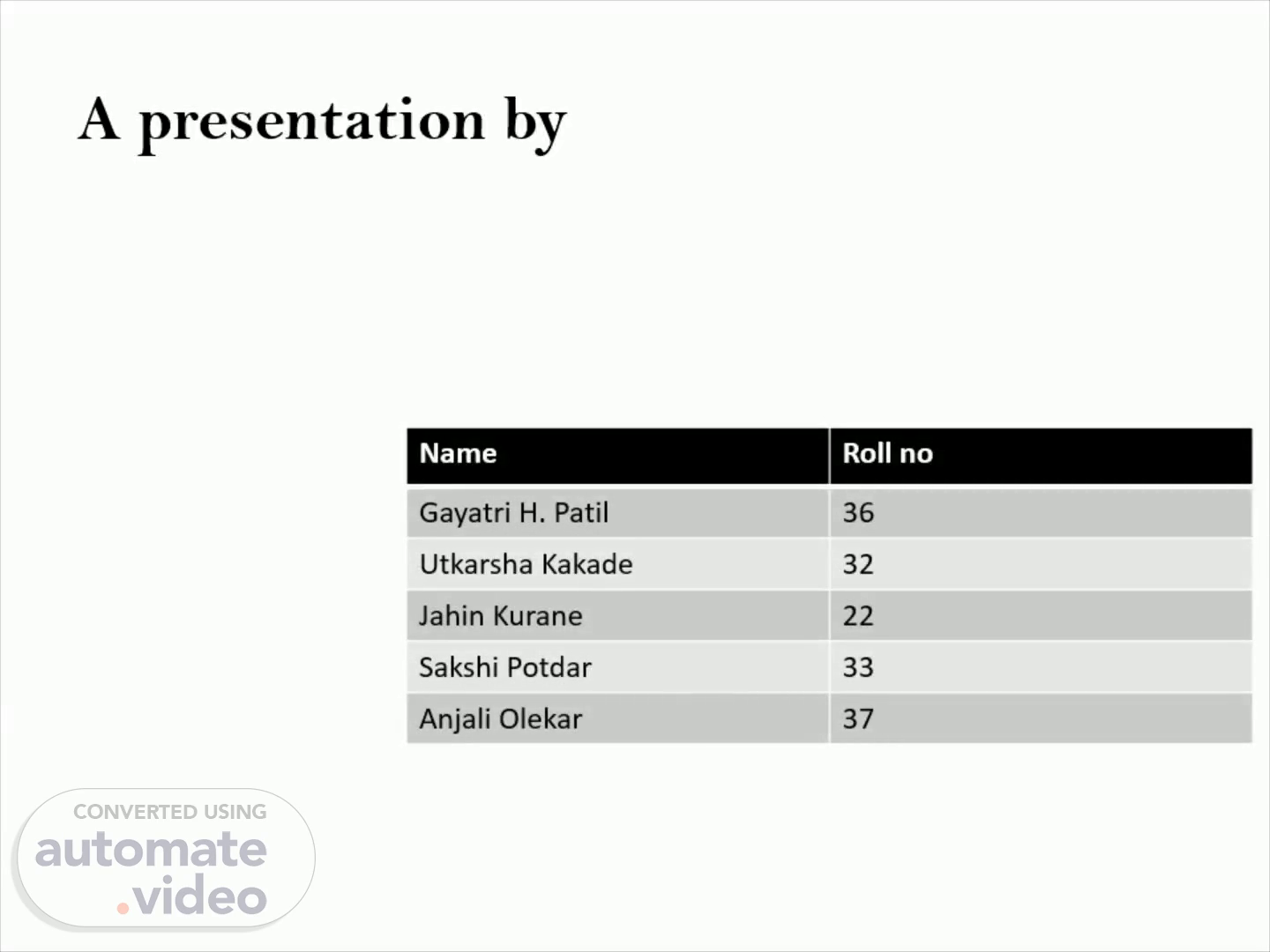
A presentation by. Name Roll no Gayatri H. Patil 36 Utkarsha Kakade 32 Jahin Kurane 22 Sakshi Potdar 33 Anjali Olekar 37.
Scene 2 (10s)
F.W.TAYLOR. “ The Father Of Scientific Management” And The Evolution Of Management Theory.
Scene 3 (34s)
. Frederick W. Taylor, in full Frederick Winslow Taylor, (born March 20, 1856, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S.—died March 21, 1915, Philadelphia), American inventor and engineer who is known as the father of scientific management. His system of industrial management, known as Taylorism, greatly influenced the development of industrial engineering and production management throughout the world. Taylor was the son of a lawyer. He entered Phillips Exeter Academy in New Hampshire in 1872, where he led his class scholastically. After passing the entrance examination for Harvard University, he was forced to abandon plans for matriculation, as his eyesight had deteriorated from night study. With sight restored in 1875, he was apprenticed to learn the trades of patternmaker and machinist at the Enterprise Hydraulic Works in Philadelphia. Three years later he went to the Midvale Steel Company, where, starting as a machine shop labourer, he became successively shop clerk, machinist, gang boss, foreman, maintenance foreman, head of the drawing office, and chief engineer..
Scene 4 (1m 35s)
abstract. Fredrick Taylor. Mechanic engineer and management consultant. Factorise were springing up everywhere and standardized way did not yet exit to manage large groups of people and handle increasingly complex work . Taylor wanted to make organization more standardized, efficient and productive by studying their work process closely..
Scene 5 (2m 2s)
TO DO. Scientific Management. Applying science to work =studying task carefully and systematically at micro level to speed up work . Wanted to break away from the common sense "Rule of thumb" that he saw as unproven and inefficiency Scientific management is also known as Taylorism..
Scene 6 (2m 19s)
Division of labour. . Wanted to divide work process into small, simple and simple steps= Division of labour. Each step or two was performed by a different person. Wanted to determine the best way a standard to do every part of every task to boost productivity.
Scene 7 (2m 43s)
Wanted to clear the chain of command authority structure that seperated the manager from worker . Manager would design work process and enforced how the work was performed. Employee simply followed direction ..
Scene 8 (3m 5s)
Principles Of Scientific Management. . . Replacing rule of thumbs with science. Obtaining harmony on group action rather than discord on group action. Cooperation between management and workers. Working for maximum output rather than restricted output. Development of workers through scientific selection and training.
Scene 9 (3m 23s)
Motion Study. In this study movement of body and limbs required to perform a job are closely observed. In other words. It refers to the study of movement of an operator on machine involved in a particular task . The purpose of motion study is to eliminate useless motions and determine the best way of doing the job . Motion study increases the efficiency and productivity of workers by cutting down all wasteful motions.
Scene 10 (3m 48s)
J ob it is a technique which enables the manager to ascertain standard time taken for performing a specified job. This technique is based on the study of an average workers having reasonable skill and ability. Average workers is selected and selected and assigned the job and then with the help of a stop watch . time is ascertained for performing than particular job..
Scene 11 (4m 14s)
Standardization. It implies the physical attitude of product should be such that it meets the requirements & needs of customers. Taylor advocated that tools & equipments as well as working conditions should be standardization to achieve standard output from workers. Standardization is a means of achieving economics of product. Standard of performance are established for workers at all levels..
Scene 12 (4m 34s)
Various other techniques have been developed to create ordeal relationship between management and also to create better understanding on part of works. Those includes use of instruction cards, strict rules & regulations, graphs, slides, charts etc , so as to increase efficiency of workers..
Scene 13 (4m 51s)
Differential Piece Wage Plan. This tech of wage payment is based on efficiency worker. The efficient workers are paid more wages than inefficient one. This system is a source of incentive to workers who importiving their efficiency in order to get more wages. It also encourages inefficient workers to improve their performance and achieve their standerds.
Scene 14 (5m 9s)
Effect of Scientific Management Techniques on today's Human Resources Management.
Scene 15 (5m 25s)
Taylor's scientific management consisted of four principles.
Scene 16 (5m 49s)
Advantages Of Scientific Management. To the employer; Higher productivity Lower cost of production Better utilisation of resources Improved quality of work. To the employee; Improvement in working conditions Higher earnings Better skills through training.
Scene 17 (6m 3s)
While scientific management principles improved productivity and had substantial impact on industry they also increase the monotony of work and in some cases the use of stop watches often was protested and led to strike. In 1911 and 1912 Taylor was questioned by a special committee of the US House of Representatives. As a result laws were passed banning the use of stop-watches by civil servants and it was only in 1949 that this restriction was lifted ..
Scene 18 (6m 34s)
. Taylor's view of the motivations of workers has had a profound influence throughout the century until the present day. There was strong criticism of this theory that treats human beings like machines and assumes that workers are only satisfied by money, Anyway Taylor's impact was so great because he developed a concept of work design, work measurement, production control and other functions. Before scientific management such departments as work study, personnel, maintenance and quality control did not exist..
Scene 19 (7m 7s)
. 1898- Bethlehem Steel Company. Tried wide ranging changes Experience laid the basis for theories of Scientific Management On October 19, 1906, Taylor was awarded an honorary degree of Doctor of Science by the University of Pennsylvania. Taylor eventually became a professor at the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth College..
Scene 20 (7m 36s)
. . Relations with ASME. Taylor's own written works were designed for presentation to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): ✓ Notes on Belting (1894), ✓ A Piece-Rate System (1895), ✓ Shop Management (1903), ✓ Art of Cutting Metals (1906), ✓ The Principles of Scientific Management (1911).
Scene 21 (8m 7s)
. Taylor's influence USA. Hugo Munsterberg created industrial psychology. Harvard University, one of the first American universities to offer a graduate degree in business management in 1908, based its first year curriculum on Taylor's scientific management.
Scene 22 (8m 37s)
. Switzerland. In Switzerland, the American Edward Albert Filene established the International Management Institute to spread information about management techniques..
Scene 23 (9m 4s)
. USSR. In the Soviet Union, Vladimir Lenin was very impressed by Taylorism, which he and Joseph Stalin sought to incorporate into Soviet manufacturing. Nevertheless, Frederick Taylor's methods have never really taken root in the Soviet Union..
Scene 24 (9m 35s)
. The basic ideas used in modern management:. Use of scientific analysis to select the best ways to perform tasks; Selection of employees that are better suited to perform the tasks of their training. The systematic use of incentive workers. Providing employees with the resources necessary to effectively perform tasks. Separation of planning and reflection on the work itself..
Scene 25 (10m 1s)
abstract. Conclusion. Taylor has substantially contributed to todays human resource management- his theories from a basis for personnel selection being one of the most important functions of personnel management Although he has been criticized for putting the human factor into the background. Taylor was effective in the development of long term employment by suggesting recruiting the personnel by means of scientific methods..
Scene 26 (10m 25s)
Thank you!. .