Page 1 (0s)
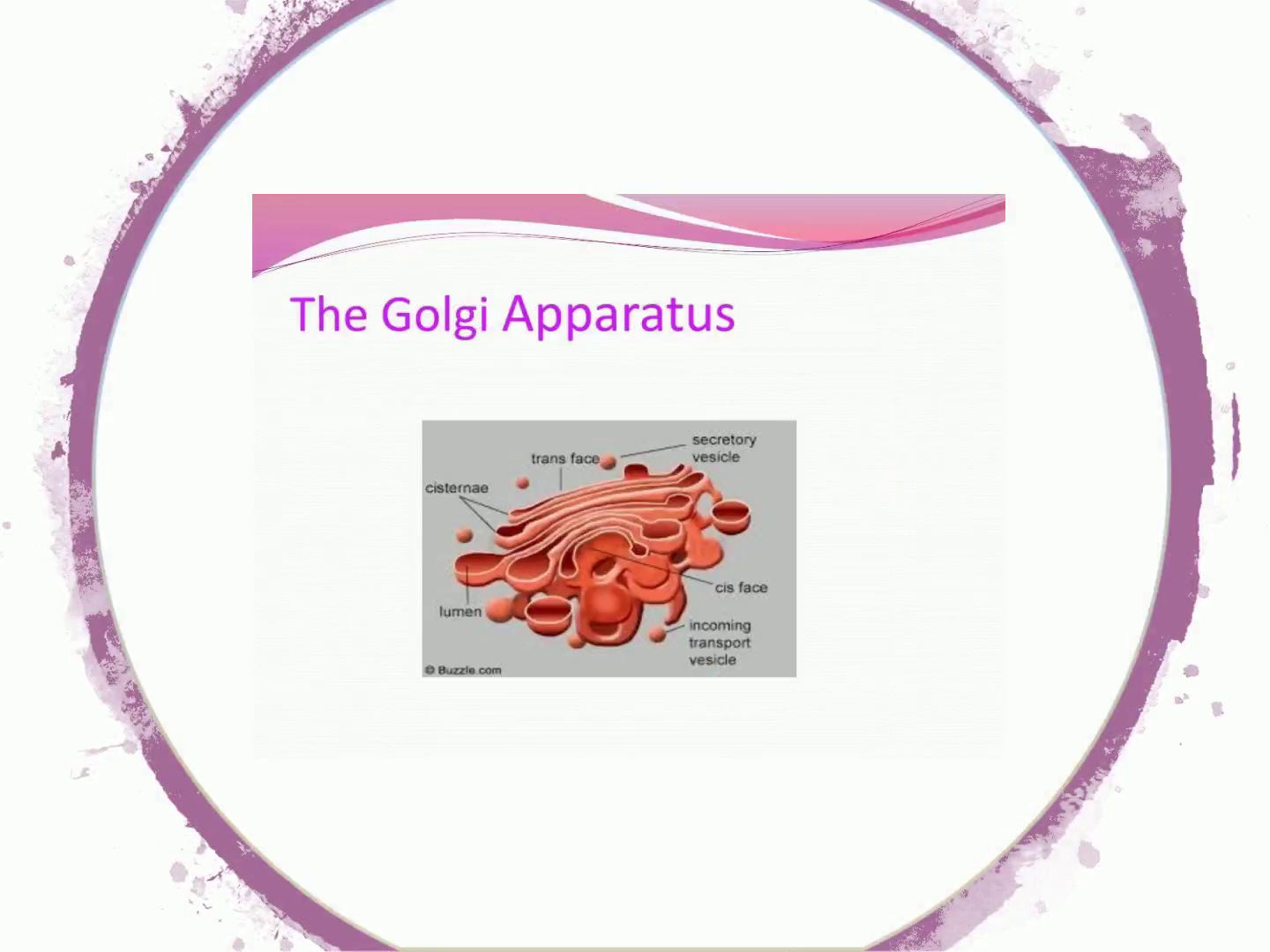
The Golgi Apparatus secretory trans face. Cis face •ncoming transport.
Page 2 (9s)
Defining: • Golgi apparatus — a group of flattened stacks of membranes ( Golgi body) • Cisternae — individual stacks of membranes ( Latin collecting vessels" • Cisternae vary in number within the golgi apparatus, depending on what kind of cell they are in.
Page 3 (24s)
Functions: • Collection of molecules • Packaging of molecules • Distribution of molecules • The synthesis of cell wall components.
Page 4 (36s)
Pa rts: • Transport vesicles — transport non synthesized materials from ER ( Endoplasmic reticulum) • Lumen — storage for materials before going to the cis face • Cis face — front, receiving end, located near ER, materials arrive via transport vesicles.
Page 5 (51s)
Pa rts: • Trans face — back, exit, materials are discharged into secretory vesicles • Secretory vesicles — carry synthesized materials to their correct location • Lysosomes - digestive vesicles, contain high levels of degrading enzymes.
Page 6 (1m 5s)
ecting, Packaging, & Distribution • Transport vesicles bring materials into the cis face, cis face synthesizes and moves materials into the trans face • Trans face sends synthesized materials into secretory vesicles which then send them into their proper locations TRANSITION VESICLES SECRETION CCLL MEMBRANE VESICLES CYTOPLASM.
Page 7 (1m 21s)
Synthesis: Cell wall components • Noncellulose polysaccharides which form part of the cell walls in plants get synthesized • After they are synthesized, they get sent to the plasma membrane, they are added to cellulose • When added to cellulose, it is assembled on the exterior part of the cell wall.