Scene 1 (0s)
[Audio] Today, I have the pleasure of discussing a technological marvel that has captivated the world and expanded our understanding of the universe—the Mars Rover. The Mars Rover serves a crucial function in the exploration of the Red Planet, and today, I will delve into its functions, origin, as well as the pros and cons associated with this incredible robotic explorer..
Scene 2 (23s)
[Audio] Origin The origin of the Mars rover can be traced back to the early days of space exploration and the desire to explore other planets in our solar system. This desire and determination to explore the red planet led to the Mars rover being created in Carnegie Mellon University in Pennsylvania. NASA created the Mars rover to search and characterize a wide range of rocks and soils for clues to past water activity on Mars. The Mars rover was also used in the Pathfinder mission and in the Vikings mission, the Pathfinder mission was an ambitious mission to send a lander and a separate rover to the surface of Mars. The successful Vikings' mission in the 1970s provided valuable insights into the Martian surface and paved the way for future exploration..
Scene 3 (1m 13s)
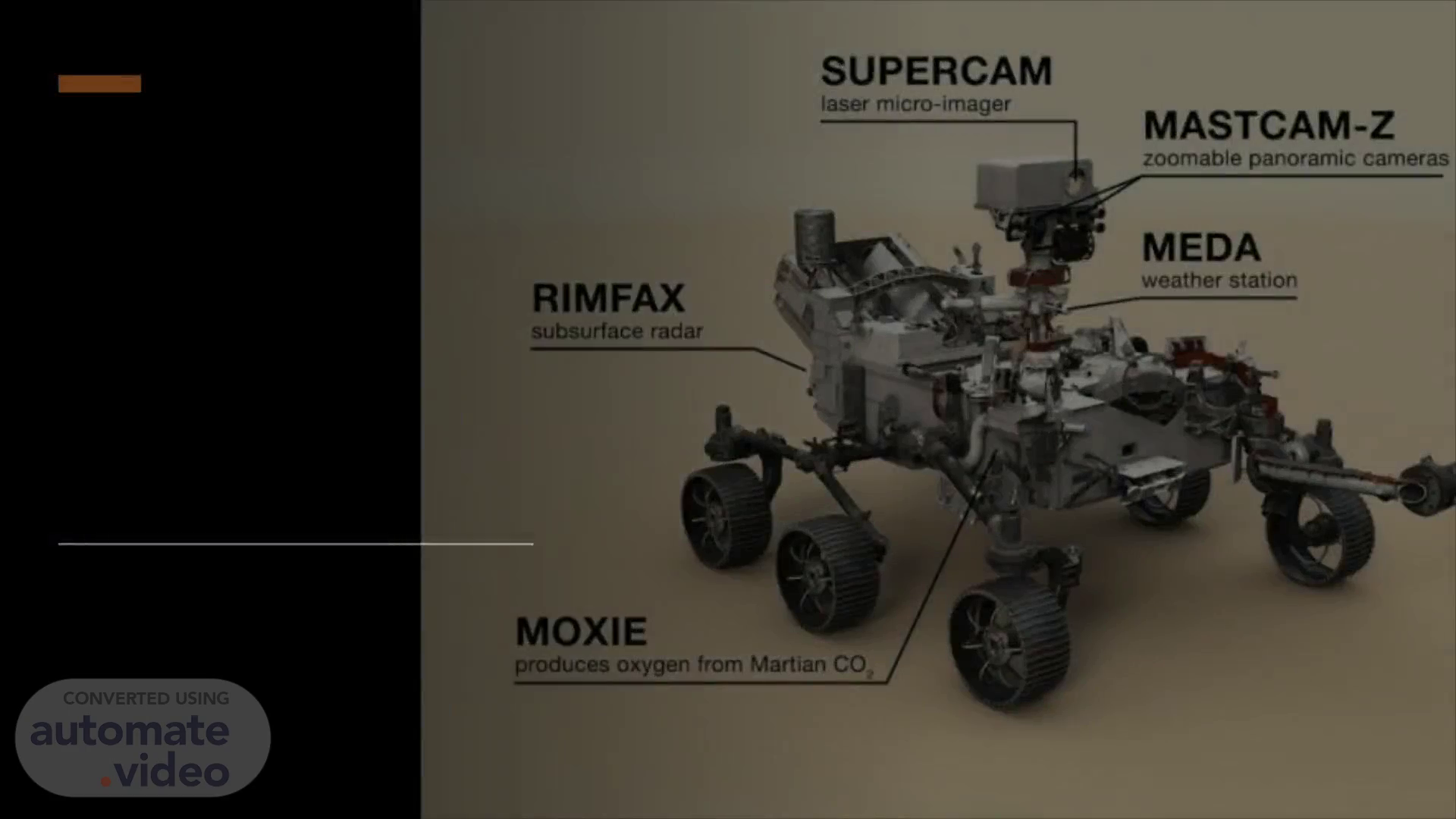
[Audio] Function The Mars rover is equipped with a suite of sophisticated instruments, one of these instruments includes the Internal Measurement Unit (IMU). This provides the rover with 3-axis information on its position which enables the rover to make precise vertical, horizontal, and side-to-side (yaw) movements. There are four main types of science instruments on the rover, these instruments are made up of other instruments, the other instruments include APXS, MAHLI, Chem Cam, Mastcam, DAN, MARDI, RAD, REMS CheMin, and SAM. These help the rover analyse all aspects of Mars. The Mars rover gets its power by using a solar panel array and an MMRTG which converts heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity, seventeen cameras at all angles of the rover, a sensor inside the rover's chassis exposed to the atmosphere, and measures changes in pressure caused by different meteorological events. A high gain antenna to send messages to NASA, six wheels to move, and much more..
Scene 4 (2m 24s)
[Audio] Positives Pros of the Mars rover is that the rover can reach extreme locations that humans cannot reach. Lower cost and fewer resources used to launch the rover than humans, unmanned space probes can effectively reach further locations that a space probe with humans. The Mars rover can effectively study rocks within a shorter time period than humans making the mars rover effective..
Scene 5 (2m 51s)
[Audio] Negatives There are many cons associated with the Mars rover, this includes the high chance of failure with unpredictable weather conditions. Mars's difficult terrain can cause the rover to easily get trapped. Can only reach a speed of 10mph making the exploration process slow. The big signal delay between NASA and the rover. Creating and launch the mars rover in a space probe is costly with an estimated cost of $ 2.5 billion dollars. Space probes that are unmanned take longer to send radio signals..
Scene 6 (3m 30s)
ChatGPT. Chat GPT.
Scene 7 (3m 37s)
Who Owns Chat GPT & Created it - MLYearning. Origin.
Scene 8 (3m 52s)
Function.
Scene 9 (3m 57s)
Positives.
Scene 10 (4m 3s)
Negatives.