Page 1 (0s)
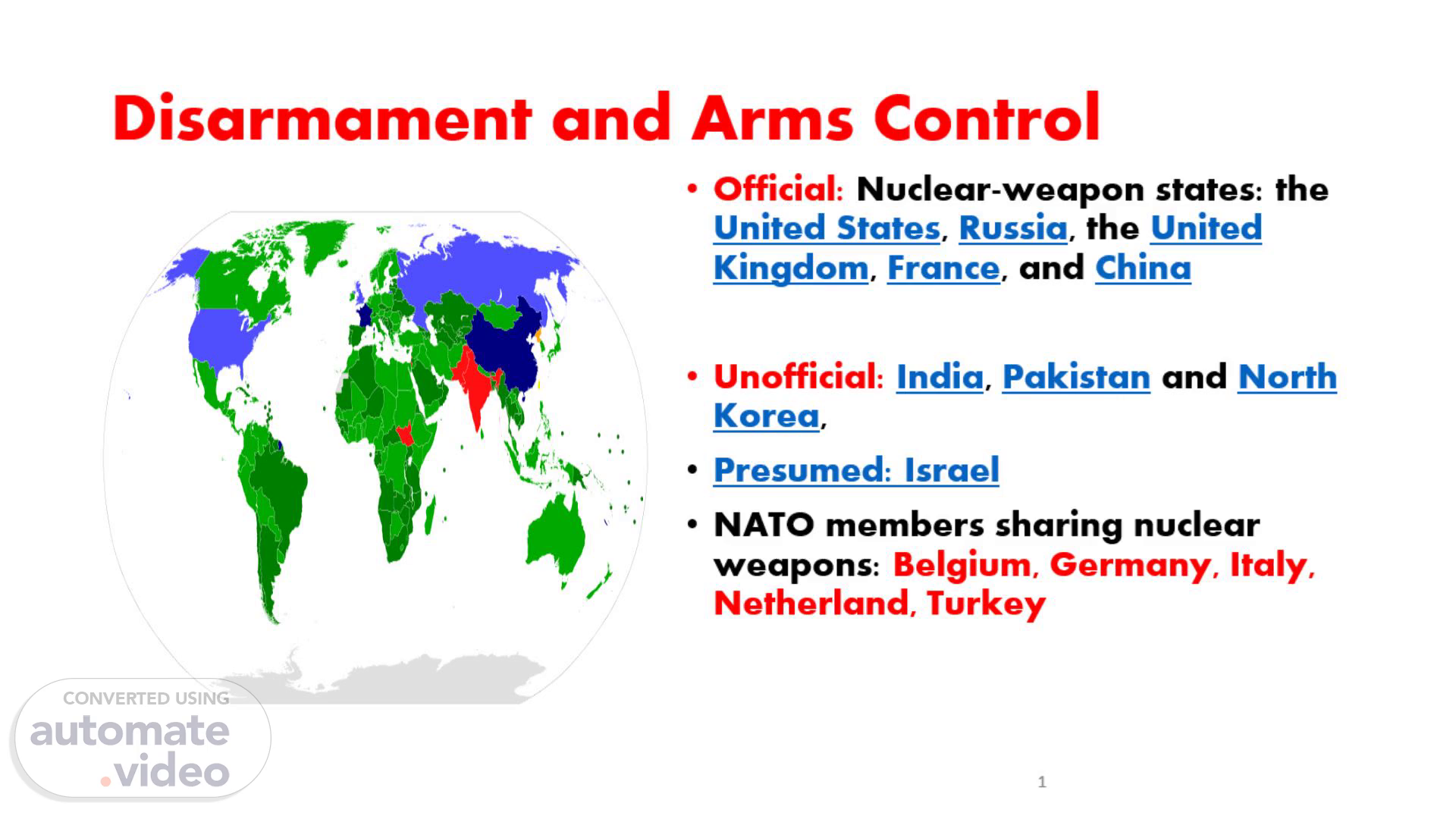
[Audio] Disarmament and Arms Control Official: Nuclear-weapon states: the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, and China Unofficial: India, Pakistan and North Korea, Presumed: Israel NATO members sharing nuclear weapons: Belgium, Germany, Italy, Netherland, Turkey.
Page 2 (20s)
[Audio] The Context Bible suggests those who live by the sword, die by the sword. GB Shaw- Nitrogen should be used for fertilizer rather than explosives Arms race drains the resources and paupers the country Nuclear proliferation issue is importance due to biological, chemical and thermo-nuclear weapons.
Page 3 (42s)
[Audio] ARMS CONTROL Arms control agreements increased due to Nuclear weapons Conventional weapons Horizontal spread of weapons.
Page 4 (54s)
[Audio] Comparisons (1) Disarmament Global destruction of weaponry and abandoning of all armed forces Arms Control It regulates the arms race for military stability It is less ambitious because it only regulates not eliminates weapons It is a relative concept Arms control is a foreign policy goal.
Page 5 (1m 16s)
[Audio] Comparisons (2) It includes multilateral and bilateral measures Conflict of interest is fact in arms control – War kept under control by adjustment of military force Disarmament is less successful than arms control Former emphasizes total elimination later limitation of weapons It implies once-for-all-solutions.
Page 6 (1m 40s)
[Audio] Arms Control – Types (1) Arms Reduction Implies mutually agreed set of arms levels of nations It may be global or regional Arms Limitation Accord to limit the outbreak of war Eg- installation of nuclear arsenal detonators in the mid air Hotline connection between heads of states.
Page 7 (2m 4s)
[Audio] Arms Control – Types (2) Moratorium on nuclear testing Sale of arms Transfer of military technology 1967- Central and South America banned nuclear weapons, Brazil and Argentina gave conditions India and Pakistan: Dimilitarisation in Sia-Chin Glasier.
Page 8 (2m 25s)
[Audio] Arms Control – Objectives (1) It can serve objectives of foreign policy and strengthen economy It can destroy nuclear weapons, reduce capabilities of weapons and risk of war.
Page 9 (2m 41s)
[Audio] Arms Control – Objectives (2) Arms control agreements led to economic and other agreements Welfare justice will be achieved by arms control (defense expenditure reduced) Political objective - reward and punish counties.
Page 10 (2m 59s)
[Audio] Disarmament Types (a) Voluntary and Compulsory Post war II disarmament voluntary North Korea, Iran, Iraq compelled for disarmament Disarmament undertaken cleverly – Central America, Central Asia and smaller nations.
Page 11 (3m 17s)
[Audio] Disarmament Types (b) Qualitative and Quantitative Qualitative: NPT, PTBT, ban on nuclear test, ban on long range missiles Quantitative: Number of Nuclear weapons Local and General Nuclear test ban – General Local -.
Page 12 (3m 37s)
[Audio] Disarmament Types (c) Comprehensive or Total Major superpowers participate but do not give commitment to do away with all weapons Total; Commitment to destroy all weapons Formal and Self-Imposed PTBT, NPT, SALT, START, CTBT – all formal Self restraint - no nuclear, no chemical, no biological weapon use by any country.
Page 13 (4m 3s)
[Audio] Obstacles in Disarmament Fear and Security Inverse relationship between disarmament and security So long fear persists, disarmament will be far cry Fear provokers arms race Vicious cycle of fear and arms race.
Page 14 (4m 20s)
[Audio] Mutual Distrust Distrust hinders agreements Disaster leads to collapse of agreements NPT, CTBT, SALT and START all not successful because of distrust Crisis of faith prevents control over arms manufacturing.
Page 15 (4m 40s)
[Audio] Political Issues and Disputes Disarmament is a political issue Countries put political issues before disarmament Arms are not cause of war, they are symptoms of political tension Can we think: Settlement of political issues without war.
Page 16 (4m 56s)
[Audio] Super Power Conflicts Super power conflicts persisted arms race Détente provided some relief to disarmament Deterioration of east-west relations in non-military areas can affect disarmament.
Page 17 (5m 12s)
[Audio] Lobby of Arms Industry Arms industry in USA, France, Russia are dictating disarmament policy. The arms industry finds benefits in war.
Page 18 (5m 23s)
[Audio] Advancement of Military Technology Race for superior quality weapons Nuclear stock pile and missiles increased after II WW New weapons used as bargaining chips in disarmament talks Possession of nuclear weapons enhances countries image, this lures smaller countries.
Page 19 (5m 44s)
[Audio] National Interest – Take much and give little No nation is ready to give much Security is dear and fear is strong.
Page 20 (5m 54s)
[Audio] The Ratio Difficult to determine the ratio of arms possession How to allot various types of arms to different countries Technology development has made old weapons outdated Demand for modernization of weapons work against disarmament.
Page 21 (6m 10s)
[Audio] Standards of Allocation of weapons Problem of comparison of weapons (SALT talks) Insincerity of super powers NPT is discriminatory, monopolistic and deceptive due to super powers.
Page 22 (6m 24s)
[Audio] A Utopia Disarmed world is a utopian concept Disarmed world would will ensure peace – Doubtful because no experience Weapons are not cause of war rather result of strained relationship.
Page 23 (6m 38s)
[Audio] Basic Questions (1) What is the guarantee, a country will not violate treaty agreement What will be the nature, power and composition of global agency for disarmament Should agency have verification power on basis of suspicion.
Page 24 (6m 54s)
[Audio] Basic Questions (2) What should be the mode of inspection – Physical,, aerial or surveillance What punishment for violators How to involve republics in arms talks – Ukraine, Kazakhstan and Belorussia..
Page 25 (7m 9s)
[Audio] Major Disarmament Treaties Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT) 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, Testing allowed underground. Green; Signed and ratified Yellow; Only signed Red: Non signatory.
Page 26 (7m 30s)
[Audio] The PTBT was signed by Soviet Union, UK, USA in 1963 Since then, 123 states have become party to the treaty. Ten states have signed but not ratified the treaty.
Page 27 (7m 44s)
[Audio] Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty (NPT) NPT objective Prevent nuclear technology, Promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, Treaty entered into force in 1970. USA, Russia: Recognized state ratifieers Green: Other ratifiers Red: Non signatories.
Page 28 (8m 8s)
[Audio] Till 2016, 191 states have adhered to the treaty, Four states : India, Israel, and Pakistan, Sudan, have not joined. Central points: States will never to acquire nuclear weapons Share the benefits of peaceful nuclear technology.
Page 29 (8m 27s)
[Audio] Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty CTBT is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, Adopted by UNGA in 1996, but has not entered into force Till now China, Egypt, Iran, Israel and the United States have signed but not ratified the Treaty; India, North Korea and Pakistan have not signed it..
Page 30 (8m 52s)
[Audio] Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty USA, Russia: Signed Others: Annex 2 not signed - Aannex 2 States formally participated in 1996 session of the Conference on Disarmament and possessed nuclear power, all of whom must ratify the Treaty. India: Non signatory.
Page 31 (9m 17s)
[Audio] Future of Arms Control (a) Containment of Global diffusion of technology to 3rd world countries Pressure on South Asia and West Asia to adopt arms control.
Page 32 (9m 29s)
[Audio] Future of Arms Control (b) Persuade India, Israel and Pakistan to Join NPT and CTBT Conclude a global Fissile Material Cut of Treaty (FMCT) Persuade a global ban on anti-personnel land mines.
Page 33 (9m 45s)
[Audio] Controlling Proliferation of Weapons Limiting number and kind of weapons Limiting destruction after war by reducing size of arsenals Banning technologies which affects balance of power; Developing CBM.
Page 34 (10m 0s)
[Audio] Major Agreements(1) The 1925 Geneva Protocol banning use of gas and biological weapons The 1959 Antarctic Treaty preventing states from using Antarctica for military purposes;.
Page 35 (10m 17s)
[Audio] Major Agreements (2) The 1972 Biological Weapons Convention The 1968 NPT limiting transfer of nuclear weapons and technologies to non-nuclear states.
Page 36 (10m 30s)
[Audio] Major Agreements (3) The 1993 Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) The 1998 Anti-Personnel Landmines Treaty (APLT)..
Page 37 (10m 44s)
[Audio] Non-Proliferation Measures The 1972 Strategic Arms Limitation Talks The 1991–92 Strategic Arms Reduction Talks The 1993 Chemical Weapons Convention The 1998 Anti-Personnel Landmines Treaty.