Scene 1 (0s)
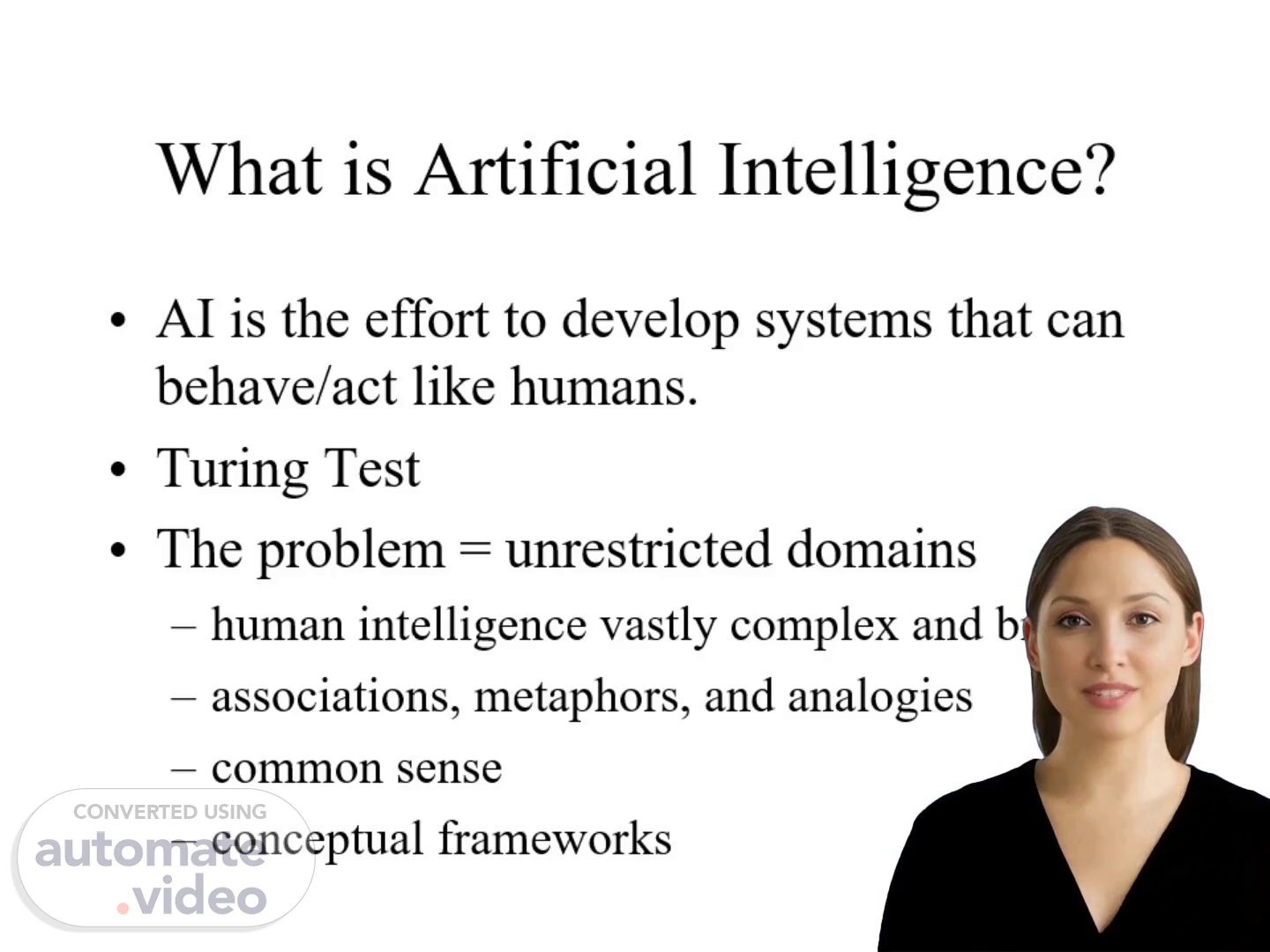
[Virtual Presenter] Artificial Intelligence is the effort to develop systems that can behave or act like humans. This concept was first introduced by Alan Turing, who proposed a test to determine whether a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. The challenge lies in creating systems that can operate effectively in unrestricted domains, where human intelligence is characterized by its complexity, breadth, and ability to form associations, use metaphors, and draw analogies. Our understanding of human intelligence also encompasses common sense and conceptual frameworks, which are essential components of human thought processes..
Scene 2 (43s)
[Audio] Artificial Intelligence consists of several distinct components, one of which is Natural Language Processing, which empowers machines to comprehend and create human-like language. This technology has numerous practical applications, including virtual assistants and language translation software. Robotics is another crucial area, where AI is utilized to program machines to execute tasks that typically necessitate human intelligence, such as assembly line work or search and rescue operations. Perceptive Systems, also referred to as Vision, enable machines to perceive their surroundings through cameras and sensors, permitting them to identify objects, track movements, and make decisions based on visual data. Furthermore, Expert Systems capture the knowledge of experts and represent it in a structured format, allowing machines to simulate human decision-making processes. Collectively, these diverse components contribute to the development of intelligent systems capable of interacting with humans in meaningful ways..
Scene 3 (1m 47s)
[Audio] Machines are intelligent when they employ constrained heuristic search. This approach enables them to focus on the most promising possibilities rather than considering all options. For instance, when playing chess, the initial move presents 20 potential choices, which increase exponentially with each subsequent move. By the seventh move, there are over one billion possible combinations. To address this complexity, machines utilize either depth-first searching, where they explore a single path extensively before backtracking, or breadth-first searching, where they examine all possible paths at a given depth before progressing to the next level. Moreover, machines possess the capacity to learn from their experiences, thereby refining their decision-making processes over time..
Scene 4 (2m 35s)
[Audio] A decision tree is a graphical representation of a set of decisions and their possible consequences. Each node in the tree represents a choice or condition, and the edges connecting them show the possible outcomes. This visual representation enables us to identify patterns and relationships between different variables. By tracing the path from top to bottom, we can forecast the outcome of a specific input based on the sequence of choices made along the way. Decision trees are frequently employed in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analysis to categorize data, make predictions, and resolve issues. They are also valuable for determining the most influential factors affecting a particular outcome..
Scene 5 (3m 18s)
Depth First Search.
Scene 6 (3m 31s)
Breath First Search.
Scene 7 (3m 44s)
[Audio] Expert Systems capture the knowledge of an expert by representing it as a rule base of if-then rules, semantic nets, hierarchy frames, and shared characteristics with IS-A relationships. This enables them to reason and make decisions based on the expert's expertise..
Scene 8 (4m 0s)
[Audio] Artificial Intelligence has led to significant advancements in various fields, including medicine and business. One notable example is the development of expert systems, which mimic human decision-making abilities. These systems have been successfully applied in several areas, such as configuring computer systems for Digital Equipment Corporation, known as DEC. Another example is the use of expert systems in the field of mining, where they have helped experts analyze data and make informed decisions. Additionally, expert systems have been used to diagnose infectious blood diseases, and even developed a successor system called EMYCIN, which was designed to handle more complex cases..
Scene 9 (4m 41s)
[Audio] An expert system shell comprises several essential components. The knowledge base represents the expertise of a specific domain, storing rules that dictate the system's behavior. These rules are essentially if-then statements describing how to apply knowledge to resolve issues. The working memory holds the facts of the current case being examined, keeping track of relevant information. The inference engine applies these rules to the current set of facts, utilizing the knowledge base and working memory to draw conclusions and make decisions. The explanation facility provides a means to explain the reasoning behind the system's choices, facilitating understanding of its decision-making process. CLIPS is an illustration of an expert system shell, serving as a software tool enabling the development and deployment of expert systems..
Scene 10 (5m 32s)
[Audio] The human brain's neural network is a remarkable example of complexity and efficiency. Over 100 billion neurons, each with thousands of connections, demonstrate its impressive architecture. Just as the brain's neurons communicate through axons and dendrites, artificial neurons exchange information through weighted connections. This similarity highlights the potential for AI to learn from the brain's incredible abilities. From recognizing patterns to making decisions, AI can draw inspiration from the intricate workings of the human brain..
Scene 11 (6m 7s)
[Audio] When impulses arrive from other neurons, a neuron starts processing information. This processing happens when the sum of these inputs reaches a specific threshold. At this point, the neuron fires, sending its own impulse to other neurons. This continuous flow of impulses enables the neuron to communicate with other neurons, ultimately allowing it to take part in complex cognitive processes..
Scene 12 (6m 33s)
[Audio] Artificial Neural Networks are designed to mimic the way our brains process information. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes, or neurons, which communicate through complex patterns of electrical impulses. These networks can learn from experience, adapt to new situations, and even recognize patterns in data..
Scene 13 (6m 53s)
[Audio] Artificial Intelligence has made significant progress in developing systems that can behave like humans. One crucial aspect of this field is Neural Networks, also known as NNs. These networks learn through a training process, where they adjust the weights on each connection based on a given dataset. Unlike traditional programming methods, NNs do not require explicit rules to function. They can operate effectively even when presented with incomplete information. However, it's essential to note that NNs lack transparency in their decision-making processes, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at certain conclusions. Furthermore, training these networks can be a time-consuming process. Despite these limitations, NNs have shown remarkable potential in various applications. We will now demonstrate a neural network in action..