Page 1 (0s)
[Audio] Hi Everybody We are here to discuss AFB So let's start.
Page 2 (8s)
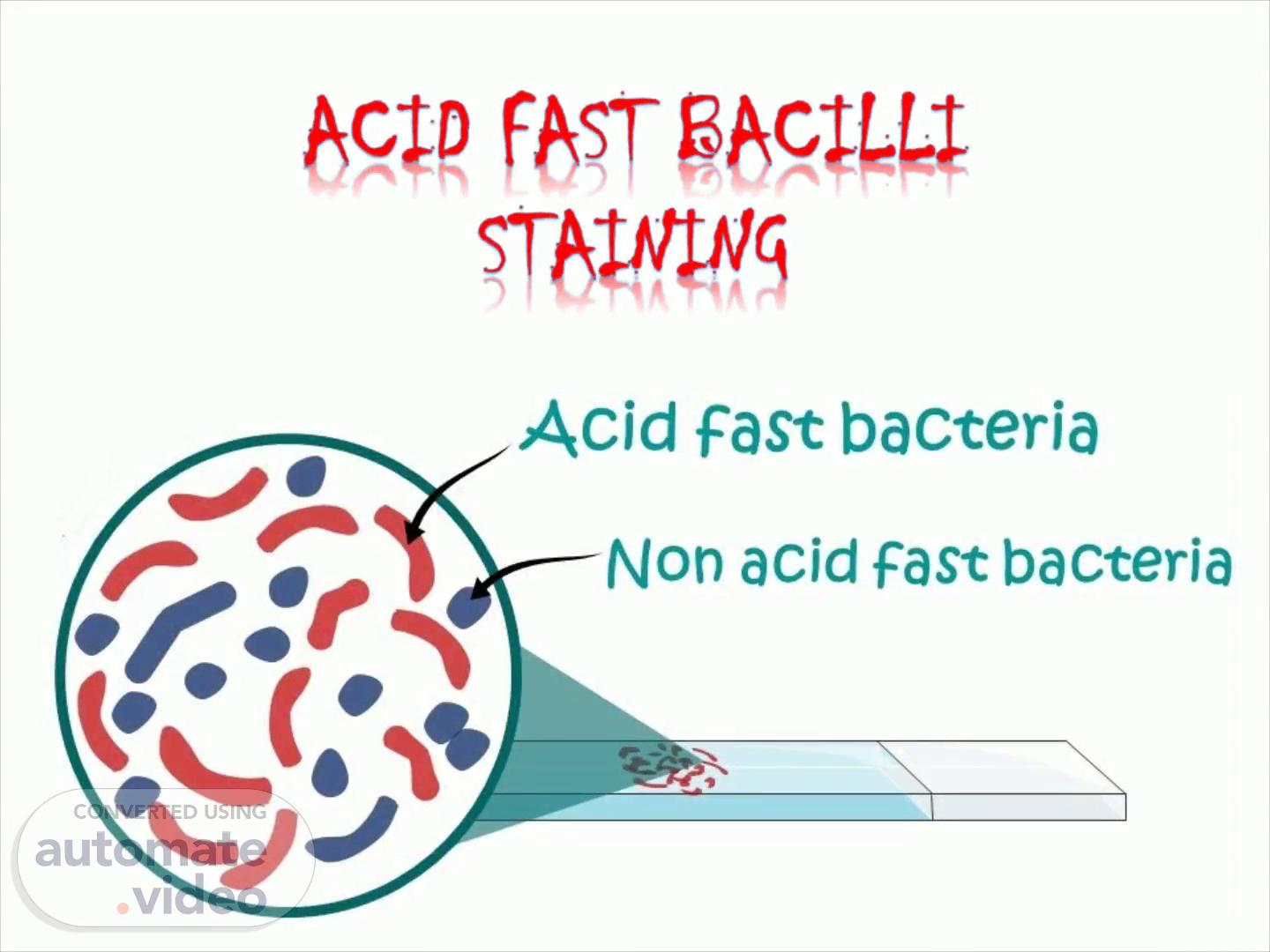
[Audio] INTRODUCTION Ziehl-Neelsen staining ( Acid Fast) technique is a differential staining technique It was initially developed by Ziehl and modified later by Neelsen hence the name Ziehl-Neelsen stain Neelsen used carbol fuchsin with heat and added a decolorizing agent acid-alcohol and counter stain methylene blue. The use of acid-alcohol in the technique so it is called as acid-fast stain.
Page 3 (39s)
[Audio] Were do we use this Ziehl-Neelsen method of staining is useful in detection of acid-fast organisms. Microorganisms that are not easily stained by basic stains such as gram staining, negative staining Examples:- Mycobacterium, Actinomycetes., Nocardia, Cryptosporidium etc. Number of bacilli in the smear may be counted and correlated with infectiousness of the person. This is important for epidemiological purpose. This is useful in following a patient's response to treatment. To know the drug resistance. If organisms fail to de-crease after therapy in the smear, the possibility of drug resistance must be considered..
Page 4 (1m 30s)
[Audio] Mycolic Acid The cause for ACID FASTNESS, In simple words, RESISTING THE ACID. These microorganisms have thick cell wall made up of lipoidal complexes known as mycolic acid Mycolic acid:- on its cell wall making it waxy, hydrophobic and impermeable Mycolic acids are beta hydroxycarboxylic acids made up of 90 carbon atoms - defines the acid fastness of the bacteria..
Page 5 (2m 3s)
[Audio] Principle How it will work The Ziehl Neelsen stain uses basic fuchsin and phenol compounds to stain the cell wall of mycobacterium species. Basic fuchsin in combination with phenol penetrates the cell wall and stains the bacilli bright red. Once stained they resist decolourization with strong acid. Mycobacterium does not bind readily to simple stains..
Page 6 (2m 34s)
[Audio] Use of heat along with carbol-fuchsin and phenol allows the penetration through the bacterial cell. The basic dye in combination with mineral acid forms a yellowish-brown compound which easily comes out of the non-acid-fast bacilli after decolourization but not out of the acid-fast bacilli. Counterstaining with methylene blue is done to form a contrast to red coloured acid-fast bacilli..
Page 7 (3m 1s)
[Audio] REAGENTS we need Ziehl-Neelsen carbol fuchsin Basic fuchsin ( powder) - 5g Phenol ( crystalline) - 25g Absolute alcohol ( ethanol) - 50ml Distilled water - 500ml Sulphuric acid - 20% - percentage may differ depends on the organism Loeffler's methylene blue - 0.5[ break]%.
Page 8 (3m 35s)
[Audio] What are the requirements Slides Spirit lamp Nichrome loop/Stick Glass marker Normal saline Distilled water Liquid Paraffin / Cedar-wood oil Gauze piece Light microscope.
Page 9 (4m 0s)
[Audio] PROCEDURE for AFB FIRSTLY WE HAVE TO PREPARE THE SMEAR FIRST Take a new slide and make an oval shaped mark at the centre by using a glass marker..
Page 10 (4m 16s)
[Audio] Make a smear from BLOOD-TINGED OR YELLOW PURULENT PORTION, remember it should be from BLOOD-TINGED OR YELLOW PURULENT PORTION of the sputum using a stick in the pre-marked area. Otherwise there will a chance of false negative.
Page 11 (4m 32s)
[Audio] Allow the smear to air-dry for 15- 30 minutes. Fix the smear by passing the slide over the flame 3- 4times..
Page 12 (4m 45s)
[Audio] Now comes the procedure of HEAT Staining 4 steps in heat staining Step one Place the slide on the staining glass rods with the smeared side facing upwards. Pour filtered CARBOL FUCHSIN over the slide so as to cover the entire slide. Wait for 5 to 8 minutes next Step two Heat the slide underneath until vapours start rising. Do not allow carbol fuchsin to boil or the slide to dry. Continue the process for five minutes. Wash both sides of the slide with tap water..
Page 13 (5m 31s)
[Audio] Step 3 Cover the slide with 20% sulphuric acid. The red colour of the preparation is changed to yellowish-brown. After about a minute in the acid, wash the slide with water, and pour on more acid. Repeat this process several times. The object of the washing is to remove the compound of acid with stain and allow fresh acid to gain access to the preparation. The decolourization is finished when, after washing, the film is only faintly pink. Decolourization generally requires contact with sulphuric acid for a total of at least 10 minutes..
Page 14 (6m 14s)
[Audio] Final step Counterstain with Loeffler's methylene blue for 15- 20 seconds. Wash with water. Place the slide in slide tray and allow it to dry. Put a drop of oil on the stained area and observe under oil-immersion ( 100X) magnification..
Page 15 (6m 36s)
[Audio] Lets Summarise Step 1 Primary stain Pool with Carbol Fuschin For 5 to 8 minutes Step 2 Mordant Fix with heating For 5 minutes Do not allow carbol fuchsin to boil or the slide to dry. Step 3 Decolorize Pool with Sulphuric Acid Repeat the process until smear turns into faint pink in colour Step 4 Counter stain Pool with Methylene Blue 15 to 20 seconds Finally air dry and observe under oil-immersion ( 100X) magnification..
Page 16 (7m 31s)
[Audio] Now comes the Modifications: A solution of 3% HCI can be substituted in place of 1% sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid solution does not decolorize as strongly as the hydrochloric acid. This makes it useful for staining organisms that are weakly acid fast, such as Nocardia. Brilliant Green may be substituted for Methylene Blue as a counter stain, resulting in non-acid fast organisms appearing green rather than blue..
Page 17 (8m 5s)
[Audio] Lets see some of the modified AFB staining Cold Method with Gabbet's methylene blue stain:- Which is widely practiced The smear is flooded with basic fuschin-phenol stain and allow to stand at Room Temperature for 10 mins and counterstain Gabbet's methylene blue stain for 2 mins. Another Cold Method Kinyoun's Method:- done for Nocardia and legionella resist decolourization by 1% cold sulphuric acid Will discuss about gabbet's and kinyoun's method in coming slide Acid fast stain using by 5% sulphuric acid:- Mycobacterium leprae resist decolourization by 5% sulphuric acid.
Page 18 (8m 53s)
[Audio] SPORE STAINING WE SHOULD KNOW Muller's method Dorner's method Schaffer fulton stain Muller chermock tergitol method What is Gabbet's Methylene blue It can be prepared with 1 Gram Of Methylene Blue 20ml Of Sulphuric Acid 30ml OF 95% Ethanol 50 ml distilled water In the next slide we will discuss about COLD method of AFB Staining with Gabbet's Methylene blue.
Page 19 (9m 34s)
[Audio] Cold Method with Gabbet's is very simple It's a 2 step procedure, as we mentioned in the earlier slide Step 1 Place the slide on the staining glass rods with the smeared side facing upwards. Pour basic fuchsin-phenol over the slide so as to cover the entire slide. Allow to stand at room temperature for 10 minutes. Wash the slide with tap water..
Page 20 (10m 8s)
[Audio] Second and final step Counterstain with Gabbet's methylene blue for 2 minutes. Wash with water. Place the slide in slide tray and allow it to dry. Put a drop of oil on the stained area and observe under oil-immersion ( 100X) magnification..
Page 21 (10m 29s)
[Audio] Another Cold Method we mentioned in earlier slide Kinyoun's Cold Method 3 step procedure The procedure for Kinyoun staining is similar to the Ziehl-Neelsen stain, but does not involve heating. The Kinyoun staining method uses carbol fuchsin as a primary stain, followed by decolorization with an acid-alcohol solution and methylene blue as a counter stain. Kinyoun carbol fuschsin has a greater concentration of phenol and basic fuchsin and does not require heating in order to stain properly..
Page 22 (11m 7s)
[Audio] RESULTS IT LOOKS VERY SIMPLE BUT WE SHOULD EXAMINE THE WHOLE SLIDE ATLEAST FOR 5 TO 10 MINUTES ACID FOR BACILLI WILL APPEAR AS BRIEGT OR PINK AGAINST BLUE BACKGROUND THE REST, that is pus, squamous epithelial cells, elastic fibres WHICH CANNOT RESIST acid will appear in blue.
Page 23 (11m 34s)
[Audio] Interpretation Acid fast bacteria retain primary dye ( Carbol fuchsin) Pink in colour Example Mycobacterium, Cryptosporidium, Nocardia, Isospora etc. Non acid fast bacteria does not retain primary dye which is Blue in colour..
Page 24 (11m 59s)
[Audio] Grading of Microscopy Smears 10 or more AFB in each oil-immersion fields is 3+ 10 or more AFB in entire smear that will be 2+ 3- 9 AFB in entire smear is 1+ 1 or 2 in entire smear will be reported as scanty.
Page 25 (12m 23s)
[Audio] How to prevent FALSE POSITIVE sputum results? Ask the patient to rinse the mouth with water before collecting sputum sample. There should not be any food particle or fibre in the sputum sample. Use only new, unscratched slides. Always use filtered carbol fuchsin. Do not allow carbol fuchsin to boil during staining. Decolourize adequately with sulphuric acid. Never touch the oil-immersion applicator to a slide. Always clean the oil-immersion lens after screening each smear..
Page 26 (13m 3s)
[Audio] How to prevent FALSE NEGATIVE sputum results? Make sure that sample contains sputum and not just saliva. There should be enough sputum (at least 2 ml). Select thick, purulent portions to make the smear. Fix the smear with correct length of time. Prepare smear with adequate material. Stain with carbol fuchsin for 5- 7 minutes. Do not decolorize with sulphuric acid too intensively. Examine every smear for at least five minutes observing at least 100 fields before recording as negative..
Page 27 (13m 45s)
[Audio] Let's start the discussion What do you mean by acid-fastness? Acid-fast bacteria do not stain readily with dilute solutions of dyes. But they, do stain when heated with a strong dye solution, and once stained they resist decolourization even by strong mineral acid..
Page 28 (14m 7s)
[Audio] The mnemonic is LMNOPQRST Legionella Mycobacterium Nocardia spp. Oocysts of Cryptosporidium parvum Protozoa (isospora, Cyclospora) Q - Nothing Rhodococcus spp. Spores, Sperm head Taenia.
Page 29 (14m 38s)
[Audio] What are the factors which affect acid-fastness of an organism? Age of colonies Medium on which growth occurs Ultraviolet light Lipid content and integrity of the cell wall of the organism.
Page 30 (14m 57s)
[Audio] Why tubercle bacilli are acid-fast? Due to the presence of mycolic acid in their cell wall..
Page 31 (15m 6s)
[Audio] Why heating of carbol fuchsin is necessary in Ziehl-Neelsen staining? Heating helps in penetration of dye (carbol fuchsin)through waxy coat surrounding the cell wall of myco-bacteria..
Page 32 (15m 21s)
[Audio] What are the other methods of acid-fast staining? Kinyoun acid-fast stain Fluorochrome stain.
Page 33 (15m 31s)
[Audio] Why Kinyoun acid-fast stain method is known as cold method? The Kinyoun stain is known as " cold stain" because the high concentration of phenol in the reagent serves to "dissolve' the lipid material in the cell wall, allowing penetration of the carbol fuchsin dye without the use of heat..
Page 34 (15m 50s)
[Audio] Which method of staining is most useful screening procedure? Fluorescent dye staining Auramine– Rhodamine stain ( AR).
Page 35 (16m 2s)
[Audio] What are the advantages of fluorescent staining over Ziehl-Neelsen staining? Fluorescent staining is More sensitive. No heating is required. Slide is scanned under low power and hence scanning is quick. Positive fluorescent smear may be re-stained by Ziehl-Neelsen or Kinyoun procedure, thereby saving the time needed to make a fresh smear. Mycobacteria appear as bright luminous yellow rods against a dark background..
Page 36 (16m 35s)
[Audio] What are the drawbacks of fluorochrome staining? Many rapid growers (e.g. Mycobacterium chelonei, Mycobacterium fortuitum) may not appear fluorescent with these reagents. Fluorescence microscope and reagents are expensive. Expert hands are required to distinguish between positive bacilli and artifacts..
Page 37 (17m 0s)
[Audio] What are the limitations of acid-fast staining? Smear must always be correlated with culture results. Organisms other than mycobacteria may demonstrate various degrees of acid-fastness. Rapidly growing mycobacteria may stain poorly or acid-fast variable..
Page 38 (17m 21s)
[Audio] What is the number of bacilli which must be present in the sputum for detection by direct microscopy? Fifty thousand to 100,000 bacilli per ml.
Page 39 (17m 34s)
[Audio] What is the minimum number of bacilli which must be present in the sputum for detection by direct microscopy while using standard concentration technique? Ten thousand/ml.
Page 40 (17m 47s)
[Audio] Can we use counterstain other than methylene blue? Yes, malachite green may be used. NEXT QUESTION What is the disadvantage of malachite green? This is a strong counterstain and may mask the presence of AFB. NEXT QUESTION Can we decolorize the smear with acids other than sulphuric acid? Yes, nitric acid or hydrochloric acid. NEXT QUESTION What is the role of phenol in carbol fuchsin? It acts as mordant. It also makes the cell surface easily penetrable for basic fuchsin by dissolving fats..
Page 41 (18m 33s)
[Audio] Which method is more sensitive ( Ziehl-Neelsen or Kinyoun)? Ziehl-Neelsen is more sensitive. Weak acid-fast strains of rapidly growing species may stain better with Ziehl-Neelsen than Kinyoun. NEXT QUESTION What is the concentration of sulphuric acid used for decolorization of various acid-fast organisms? 20% FOR MYCOBACTERIUM tuberculosis AND Atypical mycobacteria 5 % FOR MYCOBACTERIUM Leprae 1 TO 5% FOR Cryptosporidium 1% FOR Nocardia species 0.5% FOR Bacterial spores.
Page 42 (19m 20s)
[Audio] How can you differentiate smegma bacilli present in the urine from M. tuberculosis? M. tuberculosis is acid- and alcohol-fast while smegma bacilli ( commensals) are only acid-fast. NEXT QUESTION Culture medium for Mycobacterium? Lowenstein Jenson ( LJ) medium..
Page 43 (19m 47s)
[Audio] PROCEDURE FOR Specimen collection In pulmonary TUBERCULOSIS: Sputum ( 2 specimens— spot and early morning), gastric aspirate (in children) In EXTRA-PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS: Specimens vary depending on the site involved Next question Sputum Concentration methods: Modified Petroff's method ( 4% NaOH). NALC ( N-acetyl-L-cysteine) + 2% NaOH Next question Direct microscopy by acid-fast staining: Ziehl-Neelsen ( ZN) technique—long slender, beaded, less uniformly stained red color acid-fast bacilli. Kinyoun's cold acid-fast staining. Fluorescent ( auramine) staining—it is more sensitive and smears can be screened more rapidly than ZN stain.
Page 44 (20m 54s)
[Audio] What are the Molecular methods available for diagnosing tuberculosis. PCR detecting IS6110 gene. CBNAAT ( GeneXpert) and Truenat—for identification and detection of resistance to rifampicin; has a turnaround time 2 hours. Line probe assay ( e.g. Genotype TB)—for identification and detection of resistance to 1st and 2nd line ATDs; has a turnaround time of 2– 3 days..
Page 45 (21m 36s)
[Audio] What is the culture media used to grow mycobacterium Conventional culture media—take 6–8 weeks. Lowenstein Jensen ( LJ) medium—shows rough, tough and buff colored colonies in 6– 8 weeks Next question What is automated culture methods available to grow mycobacterium Automated culture methods—take 3– 4 weeks. MGIT system: Detects growth as well as resistance to antitubercular drugs ( ATDs) Next question Latest Culture identification. Automated identification—by MALDI-TOF. MPT 64 antigen detection—by ICT.
Page 46 (22m 30s)
[Audio] Morphology of the colony on LJ MEDIUM Cultures should be read within 5 to 7 days after inoculation and once a week thereafter for up to 8 weeks. COLONIES ARE Typical non pigmented, rough, dry colonies are seen on LJ medium. The green color of the medium is due to the presence of malachite green which is one of the selective agents. THESE ARE OTHER ALTERNATIVES FOR LJ MEDIUM FOR CULTURING MYCOBACTERIA.
Page 47 (23m 1s)
[Audio] Culture remains the gold standard for laboratory confirmation of TB disease, and growing bacteria are required to perform drug-susceptibility testing and genotyping. BUT THE GOLD STANDARD METHOD TAKES SEVERAL MONTHS TO CULTURE POSITIVITY A number of novel molecular technologies have in recent years to achieve quicker confirmation the diagnosis PCR CB NAAT LAMP THAT IS LOOP MEDIATED ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION LAMP is a single-tube method that is less expensive than other methods for amplifying DNA..
Page 48 (23m 45s)
[Audio] Few points on CB NAAT CBNAAT is a qualitative, nested real-time polymerase chain reaction ( PC) in vitro diagnostic test. The testing of either one or two sputum specimens by the CB NAAT may serve as an alternative to serial acid-fast stained sputum smears as an aid in the decision of whether continued infection control precautions are warranted CB NAAT also detects the rifampin-resistance associated mutations of the rpoB gene. CB NAAT IS Intended for use with specimens from patients for whom there is clinical suspicion of tuberculosis ( TB) & who have received no antituberculosis therapy, or less than three days of therapy..
Page 49 (24m 39s)
[Audio] PROCEDURE IS SIMPLE SPUTUM LIQUEFACTION AND INACTIVATION TRANSFER OF 2ML SAMPLE INTO TEST CARTRIDGE CARTRIDGE INSERTED INTO MTB TEST PLATFORM THE HANDS ON WORK WILL END HERE SAMPLE WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY FILTERED AND WASHED ULTRASONIC LYSIS OF FILTER CAPTURED ORGANISMS TO RELEASE DNA DNA MOLECULES MIXED WITH DRY PCR REAGENTS REAL TIME AMPLIFICATION AND DETECTION IN INTEGRATED REACTION TUBE FINALLY PRINTABLE TEST RESULT.
Page 50 (25m 21s)
[Audio] THIS NTEP THAT IS NATIONAL TB ELIMINATION PROGRAMME DIAGNOSTIC ALGORITHM FOR Drug sensitive TB These are the treatment algorithm There is no more category But same regime for drug sensitive patients which is first line drugs Isoniazid Rifampicin Pyrazinamide Ethambutol As initial phase And Isoniazid Rifampicin Ethambutol Continuation phase Rifampicin resistance and multi drug Resistance have to start with send line drugs And for prophylaxis Isoniazid and Rifampin or rifapentine not rifampicin Thank You Very much for patience Thank you for watching.