PowerPoint Presentation
Scene 1 (0s)
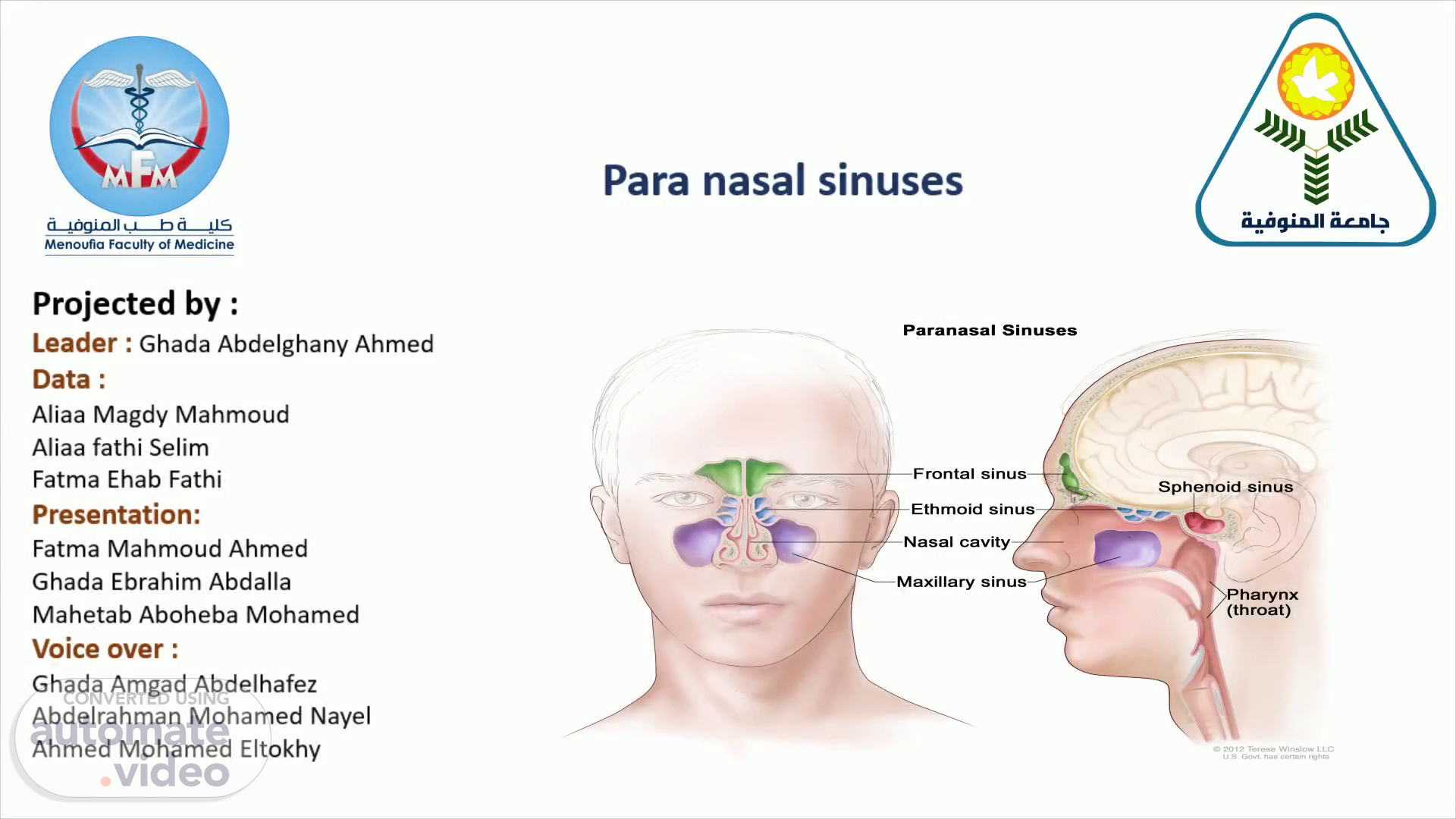
Projected by : Leader : Ghada Abdelghany Ahmed Data : Aliaa Magdy Mahmoud Aliaa fathi Selim Fatma Ehab Fathi Presentation: Fatma Mahmoud Ahmed Ghada Ebrahim Abdalla Mahetab Aboheba Mohamed Voice over : Ghada Amgad Abdelhafez Abdelrahman Mohamed Nayel Ahmed Mohamed Eltokhy.
Scene 2 (15s)
ILOS : By the end of this presentation we may know : 1- what are paranasal sinuses and their sites . 2- wall of each sinus. 3- arterial supply of each sinus. 4- venous drainage of each sinus. 5- lymphatic drainage of paranasal sinuses. 6- where paranasal sinuses open. 7- sinusitis ( it's definition, types ,symptoms, complications and treatment)..
Scene 3 (34s)
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. - They are frontal , ethmoidal ,sphenoidal and maxillary sinuses housed within the bones of the same name . - They all open into the lateral wall of nasal cavity. Function : 1- Warm and humify the inspired air. 2- reduce the weight of the skull. 3- add some resonance to the voice..
Scene 5 (2m 40s)
Diagram Description automatically generated. Site of paranasal sinusess : 1-Maxillary under the eyes in the maxillary bone. 2-Frontal sinuses superior to the eyes in the frontal bone . 3-Ethmoidal sinuses between the eyes and the nose . 4-Sphenoidal sinuses in the sphenoid bone..
Scene 6 (3m 0s)
Diagram Description automatically generated. Nerve supply : They are all innervated by branches of the trigeminal nerve Maxillary : by the maxillary nerve 2) frontal : by the opthalmic nerve 3) Ethmoidal : by the ethmoidal nerves, which branch from the nasociliary nerve of the ophthalmic nerve 4) Sphenoidal : by the opthalmic and maxillary nerve.
Scene 7 (3m 27s)
Superior canal Mo.riltary *inas First and pre— molars canines Lateral and medial inctsors ond inferior.
Scene 8 (3m 47s)
Frontal sinuses Anterior wall : forehead Superior and posterior walls : anterior cranial fossa Inferior wall : bony orbit.
Scene 9 (4m 0s)
Sphenoidal sinuses Anterior wall : nasal cavity Superior wall : hypophyseal fossa Inferior wall : nasopharynx.
Scene 10 (4m 10s)
Ethmoidal sinuses Superior wall : anterior cranial fossa, frontal bone Lateral wall : bony orbit Medial wall : nasal cavity.
Scene 11 (4m 22s)
The frontal sinus : supplied by the supraorbital and supratrochlear arteries of the ophthalmic artery. maxillary sinus: Supplied by three arteries (the posterior superior alveolar, infraorbital, and posterior lateral nasal arteries ).
Scene 12 (4m 57s)
The sphenoid sinus is supplied by the sphenopalatine artery, except for the planum sphenoidale, which is supplied by the posterior ethmoidal artery..
Scene 13 (5m 16s)
Ethmoidal air sinus : 1-anterior and middle ethmoidal sinuses : supplied by anterior ethmoidal artery 2- Posterior ethmoidal sinus: supplied by posterior ethmoidal artery.
Scene 14 (5m 47s)
The paranasal sinuses are divided per their drainage systems into 1- anterior sinuses group : (maxillary, anterior ethmoidal and frontal sinuses) 2- posterior group : ( sphenoidal and posterior Ethmoidal) - The frontal group vasculature consists of ophthalmic and supraorbital veins . - The posterior group in the maxillary vein ..
Scene 15 (6m 33s)
Diagram Description automatically generated.
Scene 16 (7m 1s)
Opening of Paranasal sinuses - Sphenoidal sinuses open in the sphenoethmoidal recess. - Posterior Ethmoidal in the superior meatus. Middle meatus : 1) bulla Ethmoidalis : receives drainage from middle Ethmoidal air sinus 2) hiatus semilunaris: Its anterior part receives from anterior Ethmoidal and frontal sinuses. 3) Its posterior part receives from maxillary sinus.
Scene 17 (8m 2s)
A picture containing text, x-ray film Description automatically generated.
Scene 18 (8m 28s)
Diagram Description automatically generated. Applied anatomy on paranasal sinuses (sinusitis) :.
Scene 19 (9m 24s)
Symptoms : symptoms often include: 1-Thick, yellow or greenish mucus from the nose (runny nose) 2-Blocked or stuffy nose (congestion) causing difficulty breathing through your nose 3-Pain and swelling 4-Headache 5-Cough 6-Bad breath 7-Fatigue 8-Fever.
Scene 20 (10m 13s)
X-ray that show maxillay sinusitis.
Scene 21 (10m 29s)
Complications Acute sinusitis complications are uncommon, and serious complications are rare. - If they occur, complications might include: - Acute sinusitis may be chronic sinusitis. (Chronic sinusitis lasts longer than 12 weeks). -Meningitis: this infection causes inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding your brain and spinal cord. -Other infections : Uncommonly, an infection can spread to the bones (osteomyelitis) or skin (cellulitis). -Vision problems: If the infection spreads to your eye socket, it can cause reduced vision or even blindness that can be permanent..
Scene 22 (12m 17s)
Treatments to relieve symptoms : Your doctor may recommend treatments to help relieve sinusitis symptoms, including: 1-Saline nasal spray : which you spray into your nose several times a day to rinse your nasal passages. 2-Nasal corticosteroids : These nasal sprays help prevent and treat inflammation 3-Decongestants : Use nasal decongestants for only a few days. Otherwise they may cause the return of more-severe congestion (rebound congestion). 4- Allergy medications: If your sinusitis is due to allergies, using allergy medications may help lessen allergy symptoms..
Scene 23 (13m 41s)
There are four types of sinuses and they are frontal , ethmoidal ,sphenoidal and maxillary sinuses housed within the bones of the same name . Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses . Symptoms of sinusitis are 1-Thick, yellow or greenish mucus from the nose (runny nose) -Blocked or stuffy nose (congestion) causing difficulty breathing through your nose-Pain and swelling –Headache-Coug-Bad breath-Fatigue-Fever We can diagnose sinusitis in a clinic through symptoms and x-rays.
Scene 24 (14m 45s)
Reference. Books. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy: Seventh Edition Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, ‘Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy’ has been explaining anatomy for a third of a century, ever since the first edition published in 1985. It has now reached the 7th edition, which is currently the latest one available on the market as of 2013..